:
.
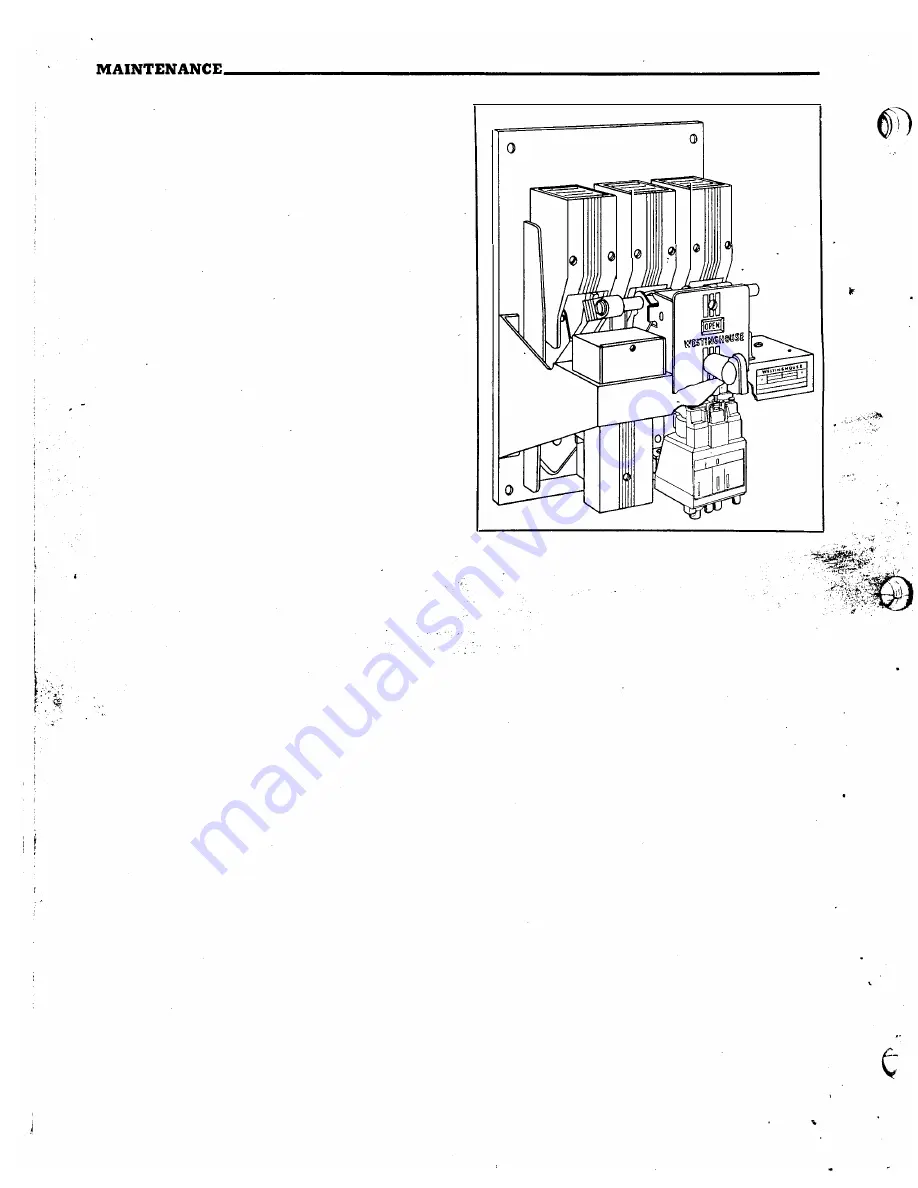
OPERATING MECHANISM
The operating mechanism (see Fig. 5)
is
non
adjustable and consists of a series of steel links de
signed to secure low closing and tripping forces.
To check for friction, raise the trip bar and slowly
rotate the manual operating handle in close and
trip direction. The linkage should follow the handle
without sticking.
The tripping load should not exceed
38
ounces
measured at the trip bar.
CLOSING SPRING ASSEMBLY
The closing spring assembly is shown in the
·breaker closed position in Fig. 5. Assuming the
breaker is in the open position, the following closing
sequence applies:
- Rotating the closing handle clockwise raises the
lift
link and lower spring guide to compress the
closing spring. Near the end of the closing stroke
the top end of the lift link strikes the first toggle
lever to start the breaker closing. As the breaker
closes the push rod raises the toggle link and push
link out of toggle which permits the closing spring
..... ·. ·'
�
to complete the breaker closing.
FIG.
6.
Overcurrent Tripping Device-Location
<.'
...
l
Slow emergency operation to check th� contact
...
·
\
sequence can be obtained by exerting a slight . signed
for
service Qn
motor
or gener
<l:!_
·'
�
ll.rpos�
closing pressure on the closing handle and simul-
feeder circuits or for service on systems 'where
· ·
taneously pushing forward on the bre'aker cross
selective overcurrent tripping
is
desired.
Figures
·"
bar to start fhe breaker closing.
-�"c.7A
and 7B shows time-current characteristics of
Maintenance.
Oil the pins and slides every
DB-15 and DB-25, circuit breakers equipped with
lO,QOO
operations.
typical overcurrent tripping devices, for selective
tripping.
CLOSING SOLENOID
The closing solenoid (see Fig.
5)
is non-adjustable.
It is designed for intermittent duty only. Check for
loose bolts.
The minimum permissible control voltages at the
terminal of the closing coil, and the closing currents
at nominal voltage are listed in Table No.2 on page 12.
OVERCURRENT TRIPPING DEVICE
The overcurrent tripping devices of the various
ampere ratings are of the same general construction
and size. They can be applied to the DB-15 circuit
breaker in ratings of 15 to 225 amperes and to the
DB-25 circuit breaker in ratings of
40
to
600
amperes.
The overcurrent tripping device can �asily be
removed from the breaker and replaced with another
unit of different rating without affecting the cali
bration.
The overcurrent tripping device, normally fur
nished for each pole of the circuit breaker, is de-
14
Construction.
The overcurrent tripping device
is of the air delayed type with all elements adjust
able. The adjustment knobs or parts likely to be
touched while making adjustments of time or pic�up
current are electrically insulated. Fig. 6A shows
a typical overcurrent tripping device ready for
mounting on .a breaker pole unit.
·
Loosening or removal of the reset valve requires
recalibration of the long delay scale.
Installation and Removal.
To install an over
current tripping device, first make sure the lower
end of the flexible conductor is in the recessed
pocket of the molded base directly above the lower
breaker stud. Then place the trip unit so that the
top terminal of the tripping device is over the
flexible conductor and the lower tripping device
terminal is over the lower breaker stud. Insert the
three bolts into the rear of the base and thread
them tightly into the terminals and molded base of
the tripping device. The mounting bolt sizes are
shown in Table No.
3.
www
. ElectricalPartManuals
. com
Summary of Contents for De-ion DB-15
Page 24: ...w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 27: ...w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 29: ...w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 31: ...w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 33: ...w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 35: ...w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 37: ...w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 39: ...w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 41: ...w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...
Page 43: ... w w w E l e c t r i c a l P a r t M a n u a l s c o m ...









































