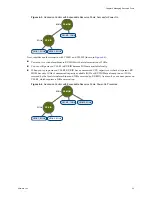
Resource Pool Creation Example
This procedure example demonstrates how you can create a resource pool with the ESX/ESXi host as the parent
resource.
Assume that you have an ESX/ESXi host that provides 6GHz of CPU and 3GB of memory that must be shared
between your marketing and QA departments. You also want to share the resources unevenly, giving one
department (QA) a higher priority. This can be accomplished by creating a resource pool for each department
and using the Shares attribute to prioritize the allocation of resources.
The example procedure demonstrates how to create a resource pool, with the ESX/ESXi host as the parent
resource.
Procedure
1
In the Create Resource Pool dialog box, type a name for the QA department’s resource pool (for example,
RP-QA).
2
Specify Shares of High for the CPU and memory resources of RP-QA.
3
Create a second resource pool, RP-Marketing.
Leave Shares at Normal for CPU and memory.
4
Click OK to exit.
If there is resource contention, RP-QA receives 4GHz and 2GB of memory, and RP-Marketing 2GHz and 1GB.
Otherwise, they can receive more than this allotment. Those resources are then available to the virtual machines
in the respective resource pools.
Change Resource Pool Attributes
After a resource pool is created, you can change its attributes.
Procedure
1
Select the resource pool in the vSphere Client inventory panel.
2
In the Summary tab Command panel, select Edit Settings.
3
In the Edit Settings dialog box, you can change all attributes of the selected resource pool.
Add Virtual Machines to a Resource Pool
When you create a virtual machine, the New Virtual Machine wizard allows you to specify a resource pool
location as part of the creation process. You can also add an existing virtual machine to a resource pool.
When you move a virtual machine to a new resource pool:
n
The virtual machine’s reservation and limit do not change.
n
If the virtual machine’s shares are high, medium, or low, %Shares adjusts to reflect the total number of
shares in use in the new resource pool.
n
If the virtual machine has custom shares assigned, the share value is maintained.
N
OTE
Because share allocations are relative to a resource pool, you might have to manually change a
virtual machine’s shares when you move it into a resource pool so that the virtual machine’s shares are
consistent with the relative values in the new resource pool. A warning appears if a virtual machine would
receive a very large (or very small) percentage of total shares.
vSphere Resource Management Guide
40
VMware, Inc.
Summary of Contents for ESX 4.0
Page 6: ...vSphere Resource Management Guide 6 VMware Inc...
Page 44: ...vSphere Resource Management Guide 44 VMware Inc...
Page 52: ...vSphere Resource Management Guide 52 VMware Inc...
Page 72: ...vSphere Resource Management Guide 72 VMware Inc...
Page 80: ...vSphere Resource Management Guide 80 VMware Inc...