HDL-64E S3
High Definition LiDAR Sensor
Page 18
Velodyne LiDAR, Inc.
©
2019
63-HDL64ES3 REV K
Upload Calibration Data
Sensors used the
.xml
file exclusively for calibration data. The calibration data found in the
.xml
file can
be uploaded and saved to the unit’s flash memory by following the steps outlined below.
1. Locate the
HDLCAL.bat
,
loadcal.exe
, and
.xml
files on the CD and copy them to the same
directory on your PC connected to the sensor.
2. Edit
HDLCAL.bat
to ensure the copy command lists the right COM port for RS-232
communication with the sensor.
3. Run
HDLCAL.bat
and ensure successful completion.
4. The sensor received and saved the calibration data.
5. Verify the successful upload of the calibration data by checking that the date and time of the
upload have been updated. Refer to Appendix E for where in the data packets this data can be
located.
You can also upload calibration data from the
.xml
file into flash memory and use GPS time
synchronization.
External GPS Time Synchronization
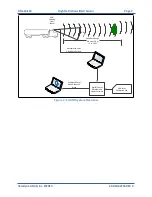
The sensor can synchronize its data with precision GPS-supplied time pulses so you can ascertain the
exact firing time of each laser in any particular packet. The firing time of the first laser in a particular
packet is reported in the form of microseconds since the top of the hour, and from that time each
subsequent laser’s firing time can be derived via the table published in Appendix H and included on the
CD.
Calculating the exact firing time requires a GPS receiver generating a sync pulse and the $GPRMC
NMEA record over a dedicated RS-232 serial port. The output from the GPS receiver is connected via a
cable to the Deutsch connector on the sensor. The sensor integrates the NMEA record into the data
packets with the corrected timestamp based on the sync pulse. The sensor data occurs at a much faster
rate than the sync pulse, so the sensor must also count the microseconds between the synch pulses
when determining the corrected timestamps. The GPS receiver needs to be supplied by the customer to
provide the required sync pulse and NMEA record.
The GPS device must have the following characteristics:
.
Issue a once-a-second synchronization pulse, typically output over a dedicated wire.
.
Configure an available RS-232 serial port to issue a once-a-second $GPRMC NMEA record.
No other output can be accepted by the sensor.
.
Issue the sync pulse and NMEA record sequentially.
.
The sync pulse length is not critical (typical lengths are between 20ms and 200ms)
.
Start the $GPRMC record between 50ms and 500ms after the end of the sync pulse.
.
Configure the $GPRMC record either in the hhmmss or hhmmss.s format.
Summary of Contents for HDL-64E S3
Page 1: ...USER S MANUAL AND PROGRAMMING GUIDE HDL 64E S3 High Definition LiDAR Sensor ...
Page 40: ...HDL 64E S3 High Definition LiDAR Sensor Page 40 Velodyne LiDAR Inc 2019 63 HDL64ES3 REV K ...
Page 41: ...HDL 64E S3 High Definition LiDAR Sensor Page 41 Velodyne LiDAR Inc 2019 63 HDL64ES3 REV K ...
Page 42: ...HDL 64E S3 High Definition LiDAR Sensor Page 42 Velodyne LiDAR Inc 2019 63 HDL64ES3 REV K ...