Chapter 4. CRAMPS/Multipulse Module Operation
67
VNMR 6.1C User Guide: Solid-State NMR
01-999162-00 C0402
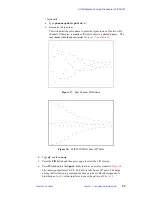
scan to scan. When set properly, a four scan phase cycle should remove both the image and
the pedestal and it should be possible to set the transmitter in the center of the spectrum.
There are no drawbacks to using the quadrature sequences instead of BR24 and MREV.
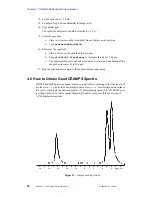
4.8 Fast MAS Assisted with a Multiple-Pulse Cycle
(WaHuHaHS)
High MAS spin rates (>15 kHz) also average
1
H-
1
H dipolar interactions and are an
alternative to
1
H CRAMPS. Used with direct polarization alone, spinning speeds
approaching 30 kHz provide line narrowing that can compare with
1
H CRAMPS. An
advantage of fast spinning is greater sensitivity. Fast-spinning spectra can be acquired with
analog filters
fb
set just greater than the spectral width for a large sensitivity improvement.
It is in fact useful to set sw equal to the spin rate to eliminate any sidebands. In contrast
multipulse methods must use open analog filters to avoid pulse ring-down, and folded noise
from the full receiver bandwidth (2-5 MHz) lowers the signal to noise.
One multipulse sequence, WaHuHaHS, can be used with fast MAS spinning. WaHuHaHS
is a semi-windowless version of the original multipulse sequence, WaHuHa. Both
sequences have a four-pulse cycle. In WaHuHaHS two of the interpulse delays are set to
zero and the total cycle time, tauc, is short enough to be used with high speed spinning. The
result is often an improvement over high-speed spinning alone or slow spinning 1H
CRAMPS.
WaHuHaHS requires the same multiple-pulse set-up procedure described above for
MREV8 and BR24.
Table 8. Multiacquisition Quadrature Corrections for MREV8
Acquisition
M(0)
Preparation Pulse (degrees)
1
(0,1,0)
90
0
2
1/
√
2(1.0,–1) 135
270
3
(0,–1,0)
90
180
4
1/
√
2(–1,0,1)
45
90
Table 9. Multiacquisition Quadrature Corrections for BR24
Acquisition
M(0)
Preparation Pulse (degrees)
1
1/
√
2(1,1,0)
90
315
2
1/
√
6(1.–1,–2)
145
220
3
1/
√
2(–1,–1,0)
90
135
4
1/
√
6(–1,1,2)
35
45