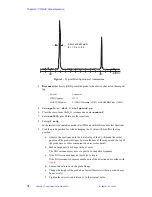
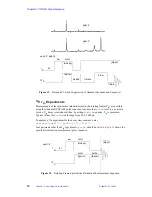
2.9 XPOLAR1—Cross-Polarization
01-999162-00 C0402
VNMR 6.1C User Guide: Solid-State NMR
40
•
tpwrm
is the observe linear modulator setting .
The parameter
tpwrm
is linearly proportional to the applied transmitter voltage—
doubling
tpwrm
halves the value of the pulse width.
•
dpwr
is the decoupler power setting for decoupling throughout the acquisition period .
•
cppwr
(UNITY only) is the decoupler power setting for cross polarization when
dblvl2=’y’.
•
dipolr
is the decoupler linear modulator setting during acquisition (0 minimum
voltage to 4095 for INOVA or 255 for MERCURY series maximum voltage). The value
of
dipolr
is linearly proportional to the applied decoupler voltage—doubling
dipolr
doubles the decoupler field strength (in kHz).
•
dblvl2
(UNITY only) is set to ‘y’ to obtain the parameter cppwr.
•
crossp
is the decoupler linear modulator setting during cross-polarization and the
initial 90
°
pulse (0 minimum voltage to 4095 for INOVA or 255 for MERCURY series
maximum voltage). The range is similar to
dipolr
. Doubling
crossp
doubles the
cross-polarization field strength (in kHz) and halves the initial proton 90
°
pulse.
•
p180
greater than 0.0 implements an additional prepulse, followed by a delay
d2
. For
direct polarization (
xpol='n'
),
p180
is an observe pulse. For cross-polarization
(
xpol='y'
),
p180
is a proton pulse.
p180
is in microseconds.
•
pcrho
greater than 0.0 implements an additional observe pulse following the contact
time. Use
pcrho
for observe T
1
ρ
measurements. The units for
pcrho
are
microseconds.
•
dm
should be set to
'nny'
. The decoupler has a maximum duty cycle of 20%.
•
pdp
set to
'y'
implements interrupted decoupling for a period
pdpd2
to cause
suppression of protonated carbons.
•
pdpd2
is set greater then 0.0 (see pdp),
pdpd2
is in microseconds
•
d2
is set greater than 0.0 (see
p180
),
d2
is in seconds.
•
srate
is the sample spinning speed, in Hz.
•
hsrotor
set to
‘y’
allows automatic update of the value of srate if automatic
spinning speed control is used.
•
toss
set to
'y'
implements timed spin echoes to suppress spinning side bands.
Timing is determined from the value of
srate
.
Note that for
toss='y'
or
pdp='y'
,
srate
must be set correctly because delays
are calculated from
1.0/srate
.
Spectrometer
Minimum Maximum
INOVAcpmas
0
4095
MERCURYcpmas
0
255
Spectrometer
Minimum, dB
Maximum, dB
INOVAcpmas
-16
63
MERCURYcpmas
0
63