NEO-M8U - Hardware Integration Manual
UBX-15016700 - R07
Design
Page 12 of 28
Production Information
☞
Consider the paste mask outline when defining the minimal distance to the next component. The
exact geometry, distances, stencil thicknesses and solder paste volumes must be adapted to the
specific production processes (e.g. soldering) of the customer.
2.4
Antenna
2.4.1
Antenna design with passive antenna
A design using a passive antenna requires more attention to the layout of the RF section. Typically, a
passive antenna is located near electronic components; therefore, care should be taken to reduce
electrical noise that may interfere with the antenna performance. Passive antennas do not require a
DC bias voltage and can be directly connected to the RF input pin
RF_IN
. Sometimes, they may also
need a passive matching network to match the impedance to 50
Ω
.
Figure 6 shows a minimal setup for a design with a good GNSS patch antenna. For exact pin
orientation, see the
NEO-M8U Data Sheet [1].
Figure 6: Module design with passive antenna
☞
Use an antenna that has sufficient bandwidth to receive all GNSS constellations. For more
information see the appendix and the
GPS Antenna Application Note [3].
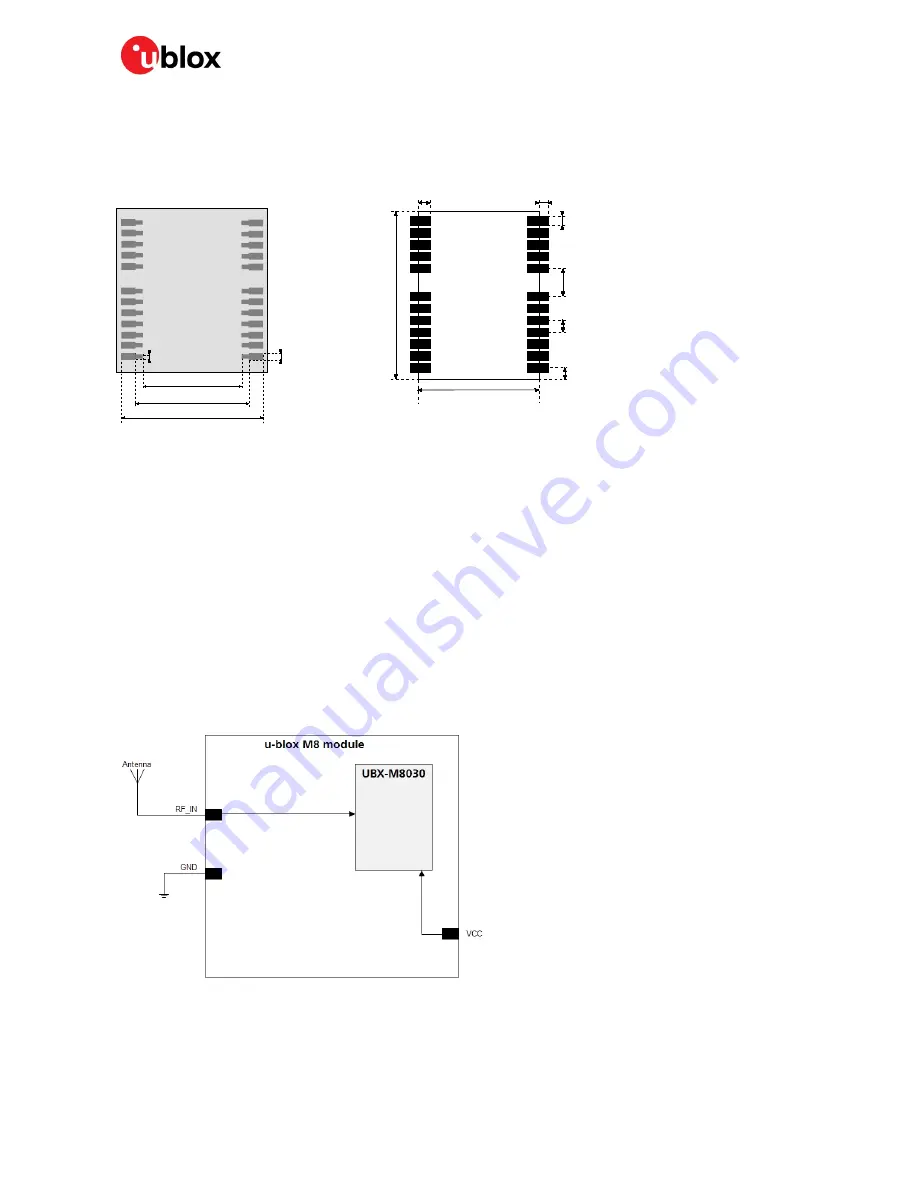
Stencil: 170
µ
m
10.4 mm [409.5 mil]
14.6 mm [575 mil]
12.2 mm [480 mil]
0.
8 mm
[31.
5
mi
l]
0.
6 mm
[23.
5
mi
l]
12.2 mm [480.3 mil]
16.
0
m
m
[
63
0
mi
l]
1.0 mm
[39.3 mil]
0
.8
mm
[31.
5
mi
l]
0.8 mm
[31.5 mil]
3
.0
mm
[118.
1
mi
l]
1
.0
mm
[39.
3
mi
l]
1
.1
mm
[43.
3
mi
l]
Figure 5: NEO-M8U footprint / NEO-M8U paste mask













































