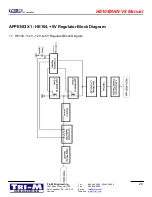
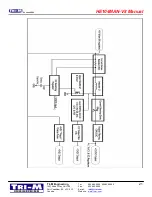
23 June 2005
HE104MAN-V8 Manual
Tri-M Engineering
Tel:
800.665.5600, 604.945.9565
1407 Kebet Way, Unit 100
Fax:
604.945.9566
Port Coquitlam, BC V3C 6L3
E-mail:
Canada
Web site:
www.tri-m.com
22
APPENDIX 2: ADVANTAGES OF USING AC TERMINATION:
One of the requirements of embedded electronics is low power consumption. One method of
reducing power is to reduce the drive current available to power the expansion bus. With over 80
signal lines, any reduction in current load would have a large impact on overall requirements. The
PC/104 Consortium Guidelines for the expansion bus specify drive current can be as low as 4mA.
Compared with the 24mA for the standard desktop computer, this is an 84 percent reduction in the
drive current available.
This disadvantage to reducing drive current is the increasing possibility for noise to infiltrate the bus.
The symptoms of noise-induced problems are often flaky or unreliable operation. Systems suffering
from noisy busses are often difficult to diagnose and solve. Programmers blame the hardware
engineers and the hardware engineers blame the software programmers.
With reduced drive currents, more attention must be paid to reducing the noise levels on the PC/104
bus. One frequently used method is bus terminators. Testing has proven the best way to terminate
the PC/104 bus is to use AC terminators instead of resistive terminators. This is the recommended
termination method for Ampro CPU products. The IEEE P996 PC Bus Standard recommends the
AC bus terminating technique.
The use of AC terminators had several advantages over DC terminators:
-
Reduced power consumption: DC terminators are typically in the 330 ohm to 1K ohm
range and draw heavy currents. This is significant when terminating the over 80 signals
on the PC/104 bus. AC terminators draw current only during the few nanoseconds when
the bus signal is changing state, resulting in negligible current drain.
-
Improved bus reliability: DC terminators invariably increase the voltage level of the logic
zero state. This decreases noise immunity, making it more likely that a zero will be seen
as a one. AC terminators do not cause this shift, resulting in a more reliable bus.
-
Reduced crosstalk: AC terminators roll off the signal transitions on the bus. The result
is a quieter bus, which has fewer high frequency effects such as crosstalk to other bus
lines.
-
Reduced EMI: Busses with AC termination tend to generate less EMI than resistively
terminated buses due to the reduction in high frequency components of signal transitions.