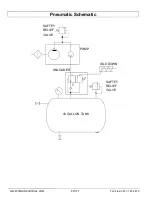
WWW.TMGINDUSTRIAL.COM
P20/27
Toll Free:1-877-761-2819
Squirt soapy water around joints during
compressor operation and watch for
bubbles. Developing bubbles indicate a
leak is present.
Tighten fittings if necessary.
Engine Maintenance
Perform engine maintenance as specified in the
engine Owner’s Manual. Items include:
Change oil after the first 20 operating hours,
and at least every 100 operating hours
thereafter and oil filter, as directed in
engine Owner’s Manual.
Failure to replace a rusted air receiver tank could
result in tank rupture or explosion, which could
cause substantial property damage, severe
personal injury, or death. Never modify or repair a
tank.
WARNING: Air tank hazards
Check Drive Belt for Tension and Alignment
WARNING: Burn hazard
Air filter check/replacement
Spark plug cleaning/replacement
Fuel filter check/replacement
Fuel tank cleaning
Change Pump Oil
After the first 50 hours of use then every 3
months or 500 hours, change pump oil while
crankcase is still warm. (See “Appendix A:
Lubricants” for suitable alternatives.)
1.
Remove the oil fill and drain plugs. Collect
the oil in a suitable container.
2.
Replace the oil drain plug and refill
compressor crankcase with clean oil.
3.
Replace the oil fill plug.
4.
Start the unit and run for several minutes.
Shut down the air compressor and
recheck the oil level. If necessary, add
more oil. (Figure 3)
Fill line
Figure 3
Drain Receiver Tank and Inspect Tank
Drain water from the receiver tank daily. Water left
in the tank can cause the tank to weaken and
corrode, increasing the risk of tank rupture. Badly
rested receiver tanks must be replaced.
Recommends a tank inspection after every 2
years of service. See “
Inspection of Unfired
Pressure Vessels
,” volumes 2-9, August 2001, Bill
McStraw (available on-line at NTIS).”
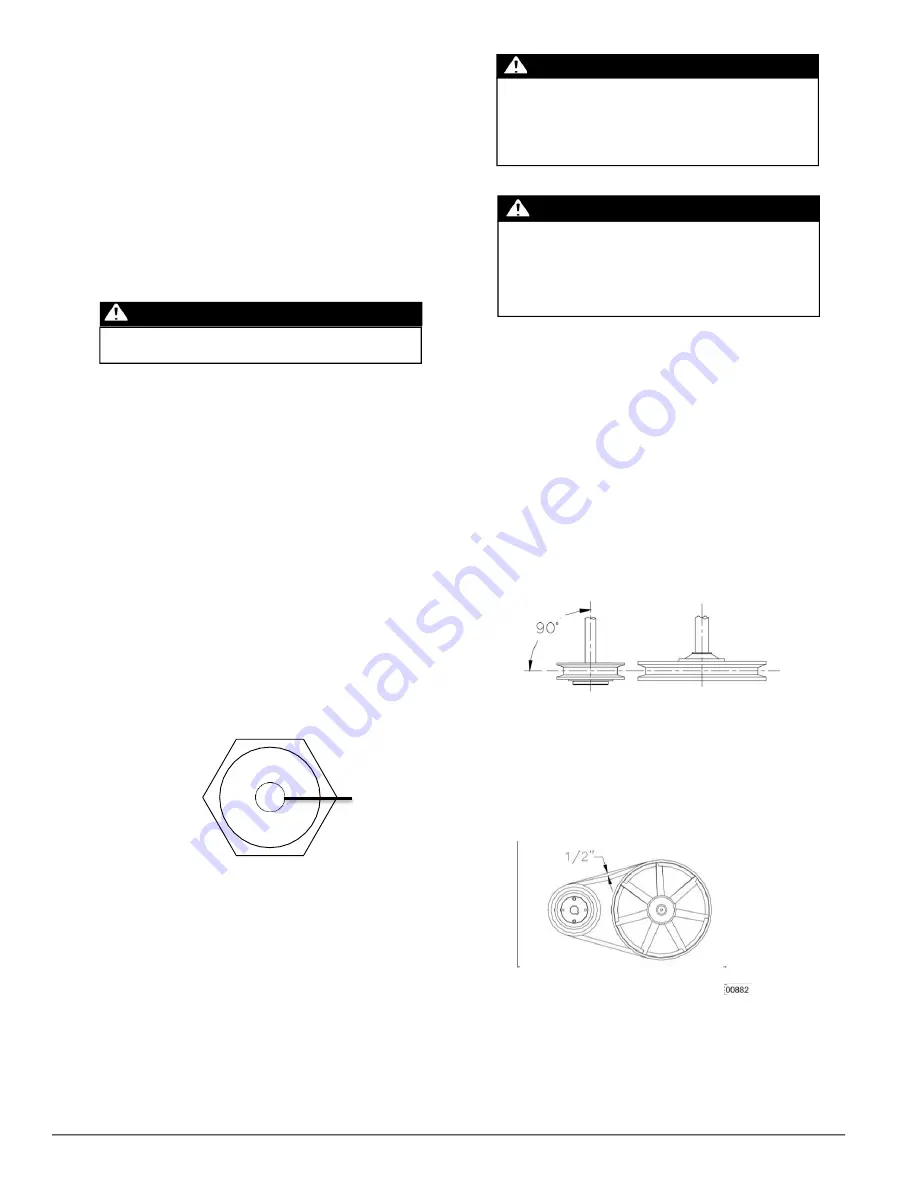
To align and adjust drive belt tension:
1.
Remove the belt guard cover.
2.
Loosen the four fasteners holding the
engine to the compressor.
3.
Shift the engine in the proper direction
The belt must be properly aligned when
adjustment is made.
4.
To align belt, lay a straight edge against
the face of the flywheel touching the rim at
two places. (Figure 4)
Figure 4
5.
Adjust flywheel or engine pulley so that
the belt runs parallel to the straight edge.
6.
If necessary, use a gear puller to move the
pulley on the motor shaft. Tighten set screw
after pulley is positioned.
7.
Check for proper belt tension. (Figure 5)
Figure 5
8.
Tighten the four fasteners holding the
engine to the top plate while tension and
alignment is maintained.
Improper pulley/sheave alignment and belt tension
can result in motor overload, excessive vibration,
and premature belt and/or bearing failure. To
prevent this from happening, check the
pulley/sheave alignmen
t
and belt tension on a
regular basis.
CAUTION: Pulley/sheave hazard
Never open oil port while engine is running. Hot
oil can spray over face and body.
Belts will stretch from normal use. When properly
ajdusted, a 5 lb. force applied to the belt between
the engine pulley and the pump will deflect the
about 1/2”.