DP83825
(RMII Master Mode)
TX_D0
TX_D1
RX_D0
RX_D1
RX_DV
TX_EN
50 MHz
DP83825
(RMII Slave Mode)
TX_D0
TX_D1
RX_D0
RX_D1
TX_EN
RX_DV
XI
XI 25 MHz
(XTAL/OsC)
System Overview
9
TIDUES1A – October 2019 – Revised February 2020
Copyright © 2019–2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated
EMC Compliant 10/100-Mbps Ethernet PHY Reference Design With IEEE
802.3at Type-1 (
≤
12.95 W) PoE-PD
to noise interference. Longer traces also act as antennas, and if run on the surface layer, can increase
EMI radiation. TI recommends keeping the trace lengths as short as possible; less than two inches is
recommended and less than six inches is the maximum.
•
Significant differences in the trace lengths can cause data timing issues. Match trace lengths for all
RMII signals within ±10 miles.
•
As with any high-speed data signal, maintaining impedance and avoiding stubs throughout the entire
data path are good design practices. Route RMII signal traces with 50-
Ω
impedance to ground.
•
To reduce the energy of digital signal sources, 50-
Ω
series termination resistors are recommended for
all RMII output signals. Note that the DP83825I device provides integrated 50-
Ω
signal terminations,
making external termination resistors unnecessary.
2.4.2
RMII Repeater Mode
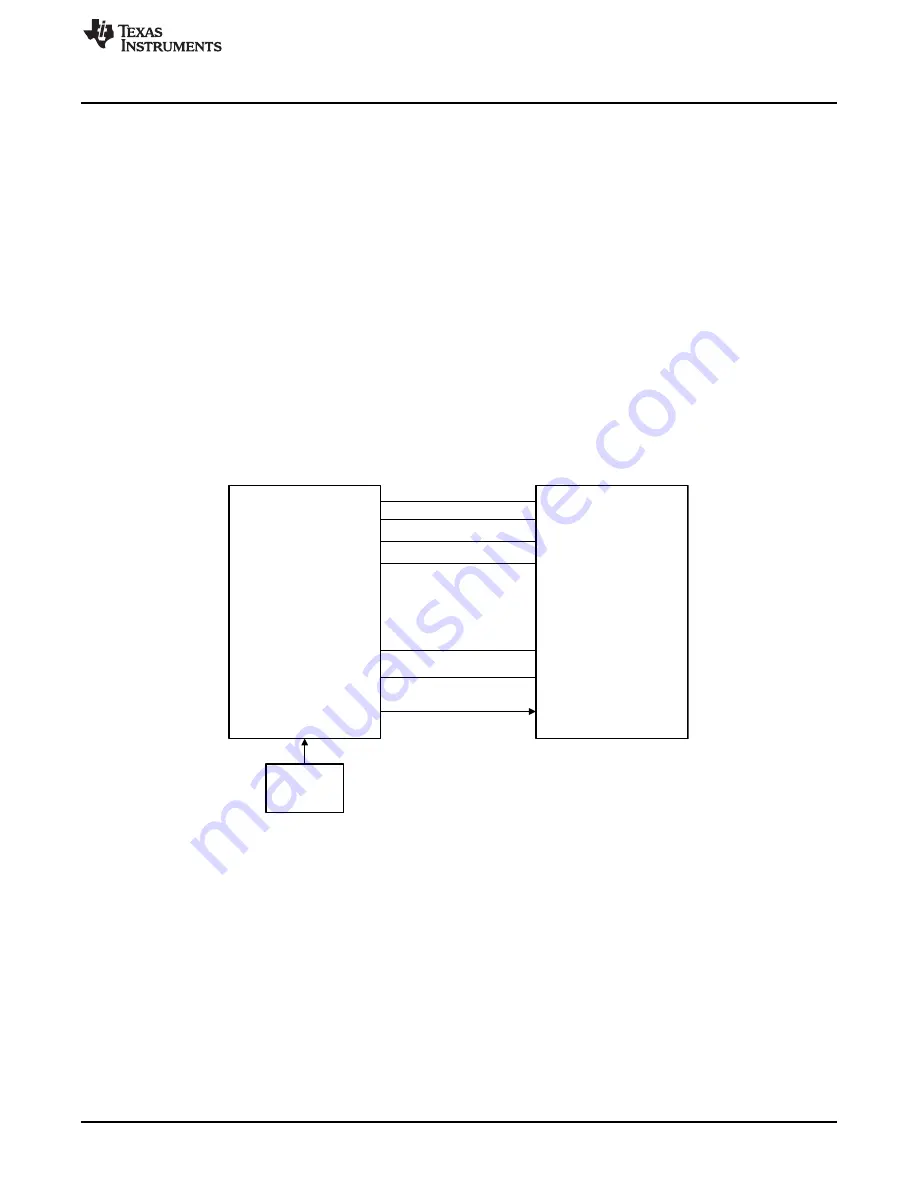
On the PSE side board, the two Ethernet PHYs (DP83822I and DP83825I) are connected in RMII repeater
mode. The DP83825I device provides the option to enable repeater mode functionality to extend the cable
reach. Two DP83825I devices can be connected in back-to-back mode without the need of any external
configuration. It provides a hardware strap to configure the CRS_DV pin of the RMII interface to the
RX_DV pin for back-to-back operation. See
for the RMII pin connection to enable the DP83825
repeater mode.
Figure 2. RMII Repeater Mode
2.4.3
Hardware Bootstrap Configuration
Hardware bootstrap configuration is a convenient way to configure an Ethernet PHY device into specific
modes of operation. Some of the functional pins are used as configuration inputs. The logic states of these
pins are sampled during reset and are used to configure the device into specific modes of operation.
Because bootstrap pins may have alternate functions after reset is de-asserted, they should not be
connected directly to VCC or GND. Pullup and pulldown resistors are required for proper operation. The
DP83822I device uses 4-level bootstraps (see
) for hardware configuration while the DP83825I
device use 2-level bootstraps (see
). See the
DP83822 Robust, Low Power 10/100 Mbps Ethernet
and
DP83825 Robust, Low Power 10/100 Ethernet Physical Layer Transceiver
data sheets for more information regarding bootstrap functionality and configuration.










































