Maintenance—
7T1
1A
Circuit
Board
Pin Replacement
It is
important
not to damage
or disturb the ferrule when
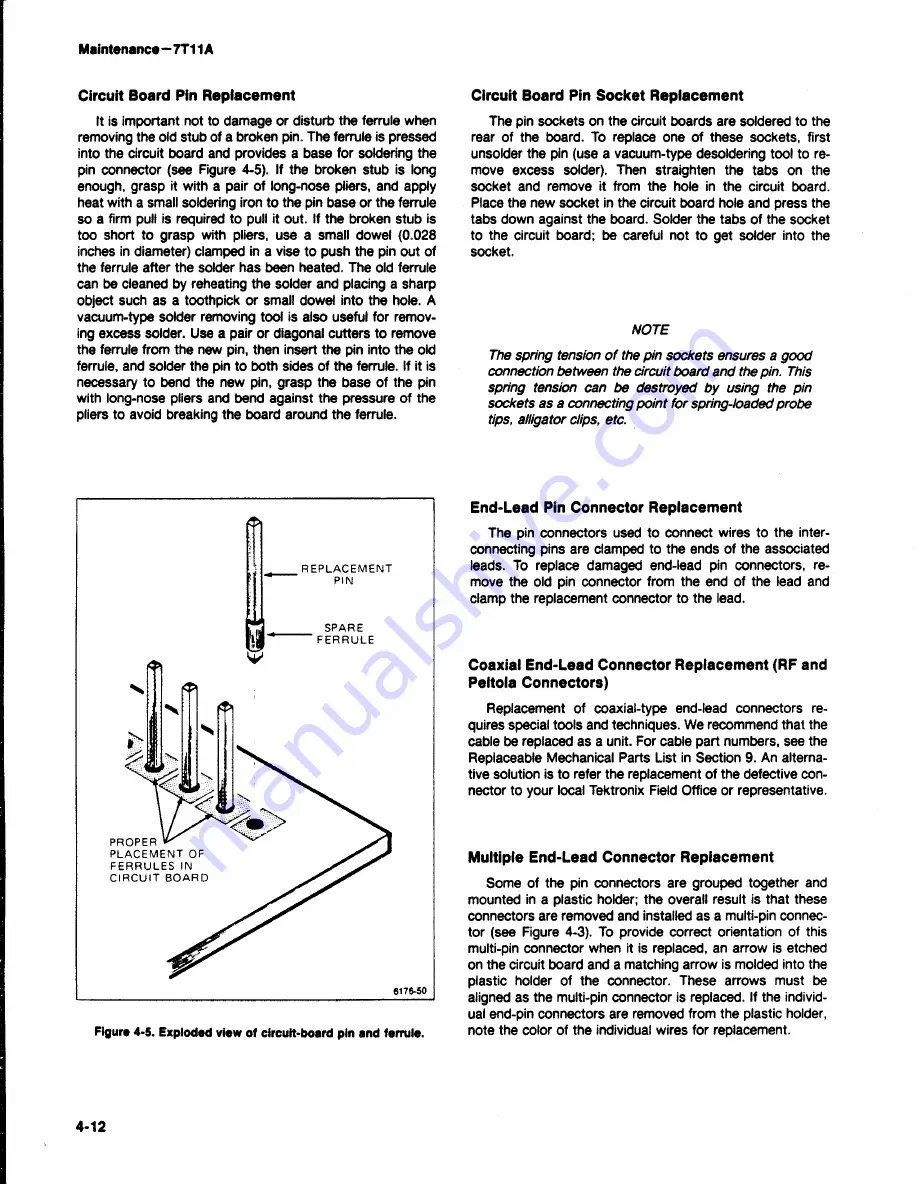
removing the old stub of a broken pin. The ferrule is pressed
into
the circuit board and provides a base for soldering
the
pin
connector (see Figure 4-5). If the broken stub is tong
enough,
grasp
it with a pair of long-nose pliers, and apply
heat
with a small soldering iron to the pin base or the ferrule
so a firm pull is required
to pull it out.
If the broken stub is
too short
to
grasp with pliers,
use a small dowel (0.028
inches
in diameter) clamped in a vise to push the pin out of
the
ferrule after
the solder has been heated. The old ferrule
can
be
cleaned by reheating the solder and placing a
sharp
object
such
as a toothpick or small dowel into the hole. A
vacuum-type
solder removing
tool is also
useful for remov
ing
excess
solder.
Use a pair or diagonal cutters to remove
the
ferrule from the new
pin, then insert the pin into the old
ferrule,
and solder
the pin to both sides of the
ferrule. If it is
necessary to
bend
the new pin, grasp the base of the pin
with long-nose pliers and bend against the pressure of the
pliers
to avoid breaking
the board around the
ferrule.
Circuit
Board
Pin Socket Replacement
The
pin
sockets on
the
circuit boards are soldered to the
rear of the board. To
replace one of these
sockets,
first
unsolder
the pin (use a vacuum-type desoldering
tool
to re
move
excess
solder). Then straighten the tabs on the
socket
and remove it from the hole in the circuit board.
Place the
new
socket in the circuit board hole and press the
tabs down against the board.
Solder the tabs of the socket
to
the circuit board;
be careful not to get solder into the
socket.
NOTE
The
spring tension of the pin sockets ensures
a good
connection
between the circuit board
and the pin. This
spring tension
can be destroyed by using the pin
sockets as a connecting
point for
spring-loaded probe
tips, alligator clips,
etc.
Figure
4-5. Exploded view of circuit-board pin and ferrule.
End-Lead Pin
Connector Replacement
The
pin connectors used to connect wires to the
inter
connecting
pins are clamped to the ends of the associated
leads.
To replace damaged
end-lead pin connectors, re
move the
old
pin connector from the end of the lead and
clamp
the
replacement connector to the lead.
Coaxial
End-Lead Connector Replacement (RF and
Peltola
Connectors)
Replacement
of coaxial-type end-lead
connectors
re
quires
special tools and techniques. We
recommend that the
cable
be replaced as a unit. For cable part numbers, see the
Replaceable
Mechanical Parts List in Section 9. An alterna
tive
solution is to refer the replacement of the defective con
nector to your local
Tektronix Field Office or representative.
Multiple
End-Lead Connector Replacement
Some
of the pin connectors are grouped together and
mounted
in a plastic holder; the overall result is that these
connectors are
removed
and installed as a multi-pin connec
tor
(see
Figure
4-3).
To provide
correct orientation of this
multi-pin
connector
when
it is replaced, an arrow is etched
on
the circuit board and a matching arrow is molded into the
plastic holder
of the
connector. These arrows must
be
aligned
as
the multi-pin connector is replaced. If the individ
ual end-pin connectors are removed from
the plastic holder,
note the color of
the
individual wires for replacement.
4-12
Summary of Contents for 7T11A
Page 10: ...7T11A Instruction Manual 7T11A Sampling Sweep Unit viii ...
Page 39: ...Theory of Operation 7T11A 3 11 ...
Page 44: ...Theory of Operation 7T11A Figure 3 11 7T11A Blanking Logic 3 16 ...
Page 47: ...Theory of Operation 7T11A Figure 3 14 Random mode block diagram 3 19 ...
Page 179: ...y TRIGGER INPUT HF Sync Selected HF Sync Selected ...
Page 180: ...THIA SAMPLING SWEEP UNIT 6176 127 ...
Page 181: ...TRIGGER INPUT J TRIGGER INPUT 6 76 127 ...
Page 182: ...7T11A A3 TRIGGER BOARD Figure 8 3 A3 Trigger circuit ...
Page 183: ......
Page 185: ...Ext Trig ...
Page 186: ......
Page 187: ......
Page 189: ......
Page 191: ...Time position CW SEQUENTIAL OV Ext Trig Time position CW RANDOM ...
Page 192: ......
Page 193: ...TIME TO HEIGHT CONVERTER 176 12 5 TIME TO HEIGHT CONVERTER s 9 ...
Page 194: ...7T11A A1 LOGIC BOARD ...
Page 195: ......
Page 197: ...1000 Ω resistor between pins 17 18 of J641 ...
Page 198: ...NOTfcS UEADLE55 CAPACITOR l FOR DECOUPLING NETWORKS SEE H THIA SAMPLING SWEEP UNIT GITG I3Ö ...
Page 199: ......
Page 200: ...7T11A A4 INTERFACE BOARD Figure 8 6 A4 lnterface circuit ...
Page 201: ...b 8 6 A4 lnterface circuit board assembly ...
Page 203: ......
Page 204: ......
Page 205: ......
Page 206: ...5 ns DIV 5 ns DIV 5 ns DIV 5 ns DIV Ext Trig 5 ns DIV ...
Page 207: ......
Page 208: ......
Page 209: ...Ext Trig ...
Page 210: ......
Page 211: ......
Page 212: ......
Page 213: ......
Page 214: ......
Page 215: ... 7TII SAMPLING SWEEP UNIT W7G 135 ...
Page 216: ...W7G 35 TIMING SWITCHES TIMING SWITCHES ...
Page 218: ...OUTPUT CONNECTORS 136 OUTPUT CONNECTORS 0 ...
Page 219: ...PARTIAL A4 INTERFACE OARD Gl7 i I37 7T11A SAMPLING SWEEP UNIT ...
Page 220: ... 137 VOLTAGE DISTRIBUTION DECOUPLING VOLTAGE DISTRIBUTION DECOUPLING H ...
Page 221: ... 174 136 1T11R SAMPLING SWEEP UNIT ...
Page 222: ...FRONT PANEL SWITCHING ...
Page 223: ...TP884 TP658 Figure 8 7 Location of Logic adjustments A2 5 im R ...
Page 231: ...12 ...
Page 232: ...FIG 1 EXPLODED VIEW 7T11A ...
Page 234: ...F IG 2 ACCESSORIES 7T11A ...