Chapter 7
Section 7.4
Implementing the HTTPS eWay JCD Sample Projects
Building and Deploying the prjHTTPServer_JCD Sample Project
HTTPS eWay Adapter User’s Guide
110
Sun Microsystems, Inc.
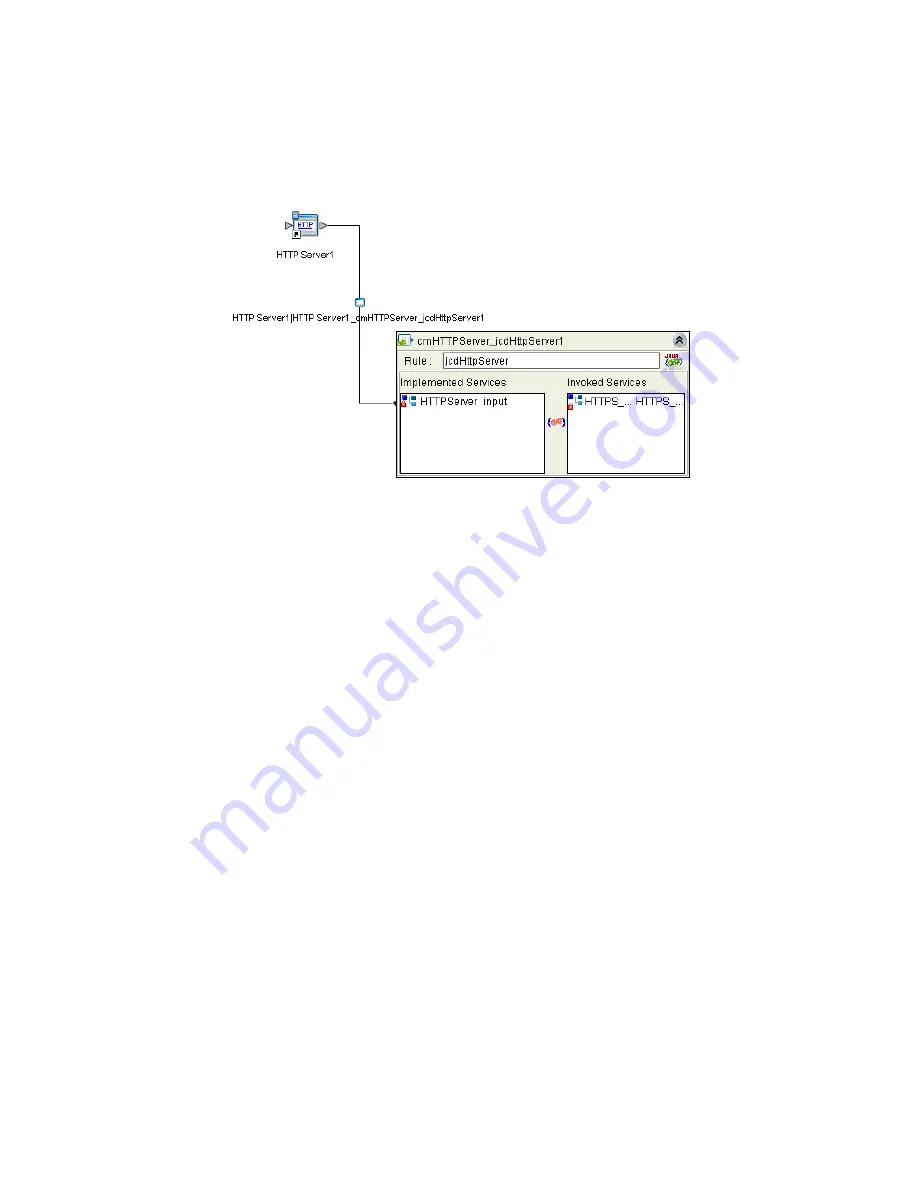
HTTPServer1
External Application in the Connectivity Map. A link is now visible
between
HTTPServer1
and
HttpServer1
, as seen in Figure 56.
Figure 56
Connectivity Map - Associating (Binding) the Project’s Components
7.4.6
Creating an Environment
Environments include the external systems, Logical Hosts, Integration Servers, and
message servers used by a Project and contain the configuration information for these
components. Environments are created using the Enterprise Designer’s Environment
Editor.
Follow the steps outlined in
“Creating an Environment” on page 78
to create an
Environment for the
prjHTTPServer_JCD
Project. For this Project, add the
HTTP
Server
external system to the Project’s Environment, and rename it
esHTTPServer
.
7.4.7
Configuring the eWays
eWays facilitate communication and movement of data between the external
applications and the eGate system. Each Connectivity Map in the The
prjHTTPServer_JCD
sample Project use two eWays that are represented as a nodes
between the External Applications and the Business Process, as seen in Figure 55.
You must configure eWay properties in both the Connectivity Map and the
Environment Explorer.
1
From the
cmHTTPServer
Connectivity Map, double-click the
HTTPServer1
eWay.
The
Properties Editor
opens to the HTTP Server External Configuration properties.
2
Modify the HTTP Server External Configuration properties by entering
HttpServerSample
in the
servlet-url
property field, and click
OK
.
For further information on configuring the HTTPS Server eWay Connectivity Map and
Environment properties, see
“eWay Connectivity Map Properties” on page 44
and
“eWay Environment Properties” on page 46
.



















