-SCS C
ONDENSER
IOM
M
ANUAL
10
STACK
AIR
FLOW
10 FT. MAX.
outlet pipes within one foot of the condenser header to prevent
undue stress on soldered connections (see Figure 4). The
refrigerant piping should be isolated by vibration isolating
supports. Provide supports (clamps or hangers) as
necessary every 5 to 10 feet along piping runs to minimize
2x
WIDTH
2x
WIDTH
vibration and noise transmission. When sealing openings in
walls use a soft flexible material to pack around the piping
20” MINIMUM
Figure 6. Walled Areas or Pits
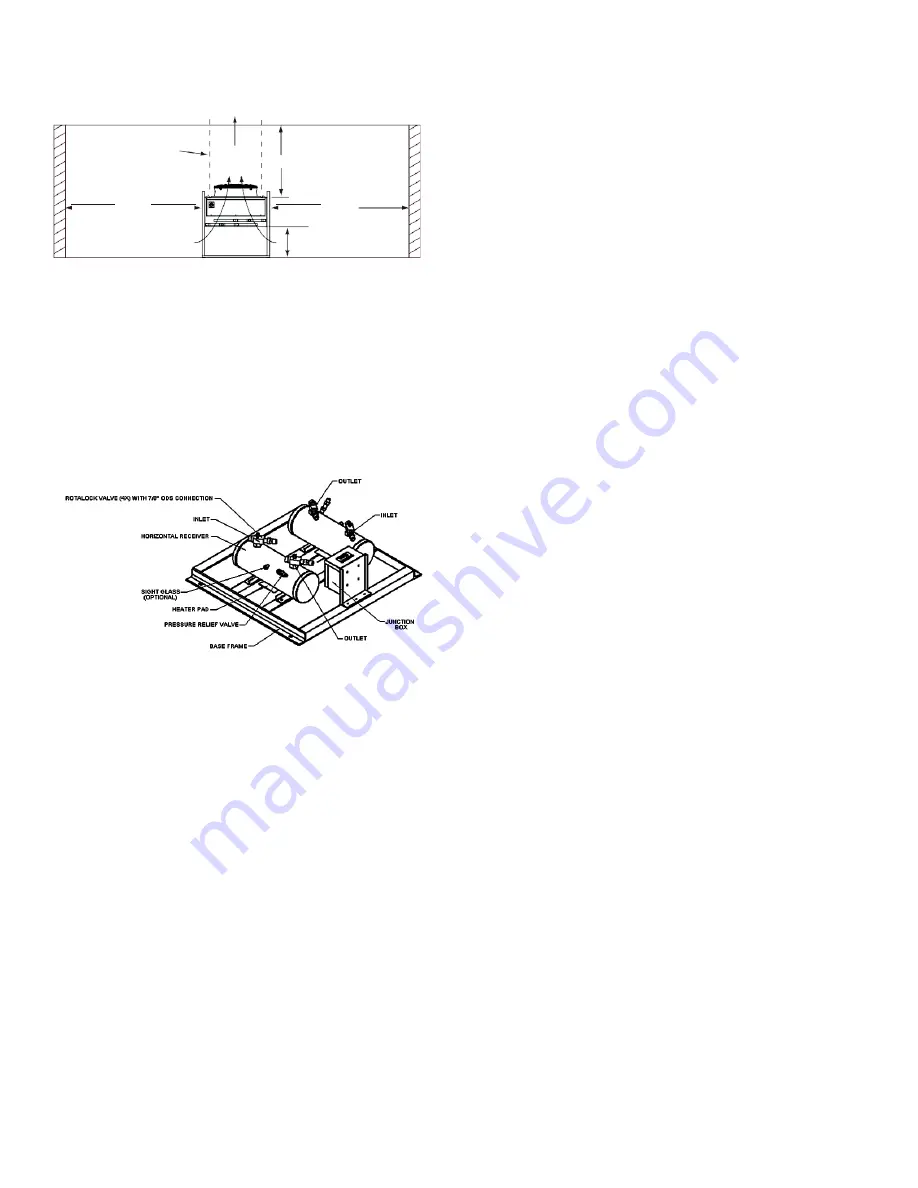
2.4.1 Receiver
Receivers are provided as an option for systems utilizing
flooded head pressure control. Receivers for SCS condensers
are provided on a separate mounting base frame. Position
optional SCS receiver(s) as close as possible to the
condenser inlet/outlet pipe stubs. Secure the receiver base
frame to the foundation using the mounting holes in the base.
(Receivers for SCS-MC condensers are factory mounted to
the condenser frame.)
Figure 7. Receiver Assembly
2.4.1.1 Head Pressure Control Valve
For SCS condensers, the head pressure control valve (HPCV)
is shipped loose for field installation. The head pressure
control valve is to be located at the condenser and brazed
in line with the piping between the condenser and receiver.
Refer to section 2.5.2. For SCS-MC condensers, the HPCV
is factory piped to the receiver.
2.5 Refrigerant Piping
Split air cooled systems require a field installed copper
discharge line and copper liquid line between the condenser
and the evaporator. Dual circuited condensers will require two
sets of piping. Refer to the refrigeration diagram provided
with your unit for piping details.
Provide a permanent stand or support brace for the inlet/
to reduce vibration transmission and prevent pipe damage.
All refrigerant piping should be installed with high temperature
soldered joints. Use standard refrigeration practices for
piping supports, leak testing, dehydration and charging of
the refrigeration circuits.
NOTE: Refer to the Copeland Applications Data Guide for
more detailed information regarding installation of
refrigerant piping.
The condenser is shipped with a dry nitrogen holding charge
which must be removed before piping and charging the
system. All refrigeration piping should be installed with
high temperature brazed joints. Use standard refrigeration
practices for piping, leak testing, dehydration and charging of
the refrigeration circuits. For copper to copper brazing (piping
liquid line or discharge line), phosphorous alloy containing a
minimum of 15% silver is recommended. General purpose
silver brazing alloy with 45% silver is recommended for brazing
dissimilar metals.
Wrap wet rags around the pipes between the areas to be
soldered and any nearby refrigeration components (such as
the optional head pressure control valve) to keep excessive
heat from traveling through the pipe and causing damage.
Clear all pipe connections of debris and prep connections for
soldering. Use only “L” or “K” grade refrigerant copper
piping. Be careful not to allow solder/piping debris to get
inside refrigerant lines. Dry nitrogen should be flowing through
the tubing while soldering at a rate of not less than 1
–
2 CFM
(0.03
–
0.6 M
3
/minute).
2.5.1
Refrigerant Line Sizing
The following general guidelines may be used to assist in
determining the size of the refrigerant lines between the
evaporator section and the remote air cooled condenser.
NOTE: Refrigerant piping between the indoor evaporator
and condenser must not exceed 150 feet (total equivalent
length). The maximum level drop from the indoor evaporator
to the condenser must not exceed 20 feet.
Refrigerant lines for split systems must be sized according
to the piping distance between the evaporator and the
















































