pool their hard drives in order to improve speed, fault tolerance, or both. RAID is
available in several different versions, commonly referred to as “levels.” The phrase
“level” suggests that there is a hierarchy between levels, which is not strictly the case.
The many implementations of RAID each have their own advantages, disadvantages,
and technical requirements. RAID can be implemented through software or hardware.
Hardware solutions are generally preferred for a higher degree of performance and
reliability.
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (Serial ATA or SATA)
Serial ATA is a relatively new method of connecting hard drives and other devices to a
computer (particularly hard drives), and is designed to replace the older IDE standard
(sometimes referred to as ATA or PATA, for Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment).
striping; striped set [of disks]
Striping is a process where two or more disks are combined and presented to the
computer as a single device (a “logical” drive): this is the process used in RAID 0.
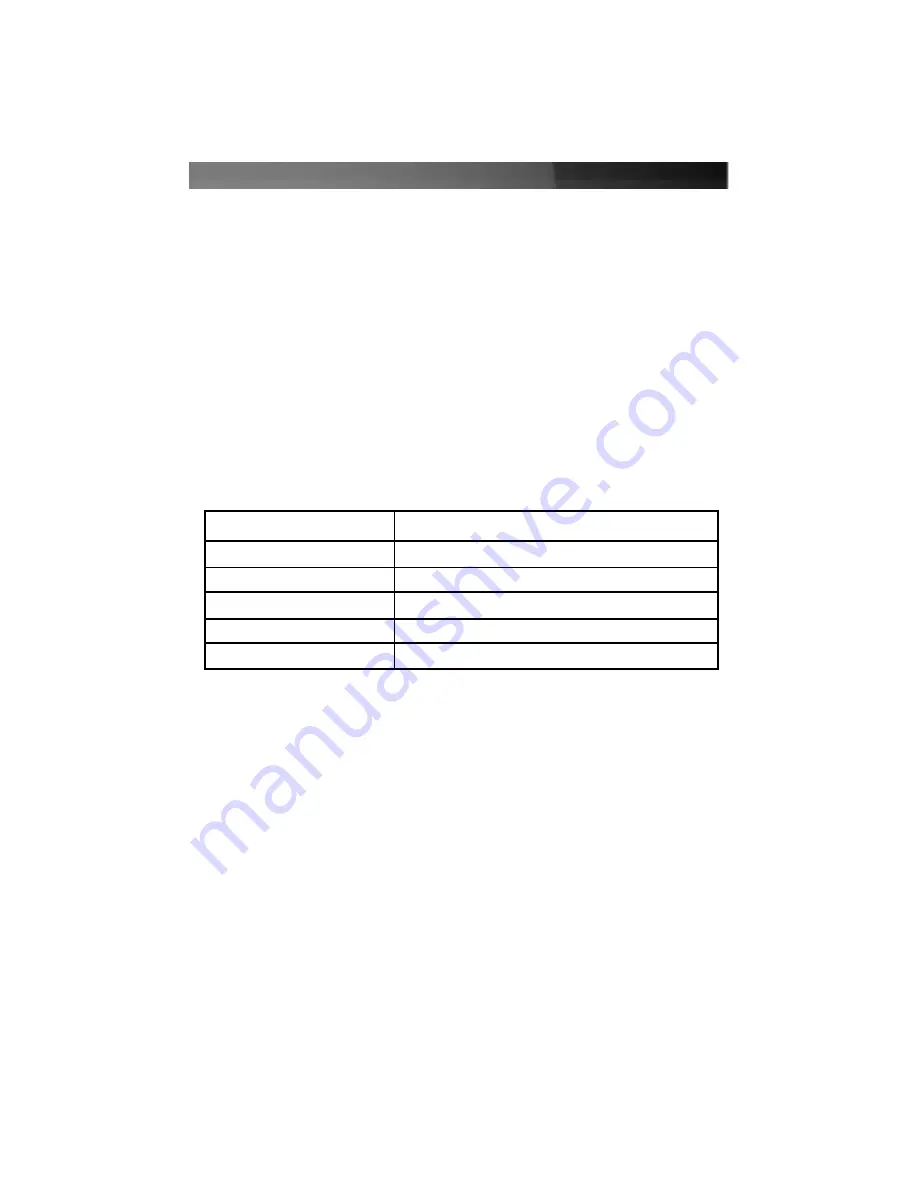
Specifications
Instruction Manual
7
Form Factor/Interface
PCI (32-bit, 33/66 MHz) or PCI-X (64-bit, 133 MHz)
Full-sized or low profile slot
Maximum Data Transfer Rate
300 MBytes/sec. (SATA II)
SATA Ports:
4 x 7-pin male (internal)
RAID Levels Supported
0, 1, 0+1, 1+S, also configurable as a typical SATA controller
OS Support
Windows NT4/2000/XP/2003 Server
Regulatory and Other Certifications
FCC Class B, CE, UL, Microsoft WHQL
Summary of Contents for PCISATA2P4
Page 13: ...Revised 5 May 2005 Rev A ...































