IM-P693-06
EMM Issue 1
5
LCS3050 Low Water Level Switch for two probes
1.3 Terms and abbreviations
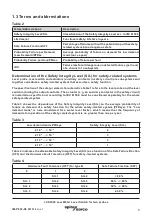
Table 2
Terms/Abbreviations
Description
Safety Integrity Level/SIL
Classification of the Safety Integrity Level acc. to IEC 61508
Lifetime (a)
Functional safety: Lifetime in years
Safe Failure Fraction/SFF
Percentage of failures without the potential to put the safety-
related system into a dangerous state
Probability Failure per Demand
(Low Demand)/PFDav
Average probability of failure on demand for low demand
mode (once a year)
Probability Failure per Hour/PFHav
Probability of failure per hour
DU
Failure rate for all dangerous undetected failures (per hour)
of a channel of a subsystem
Determination of the Safety Integrity Level (SIL) for safety-related systems
Level probe, level switch and actuators (auxiliary contactor in safety circuit) are subsystems and
together constitute a safety-related system that executes a safety function.
The specification of the safety-related characteristics Table 1 refers to the level probe and the level
switch including the output contacts. The actuator (e. g. an auxiliary contactor in the safety circuit)
is installation specific and, according to IEC 61508, must be considered separately for the whole
safety-related system.
Table 3 shows the dependence of the Safety Integrity Level (SIL) on the average probability of
failure on demand of a safety function for the whole safety-related system (PFDsys). The “Low
demand mode” is here considered for a water level limiter, which means that the frequency of
demands for operation of the safety-related system is no greater than one per year.
Table 3
Low demand mode PFDsys
Safety Integrity Level (SIL)
≥ 10
-5
... < 10
-4
4
≥ 10
-4
... < 10
-3
3
≥ 10
-3
... < 10
-2
2
≥ 10
-2
... < 10
-1
1
Table 4 indicates the attainable Safety Integrity Level (SIL) as a function of the Safe Failure Fraction
(SFF) and the Hardware Fault Tolerance (HFT) for safety-related systems.
Table 4
Hardware Fault Tolerance (HFT) for type B
Safe Failure Fraction (SFF)
0
1
2
SIL 1
SIL 2
< 60 %
SIL 1
SIL 2
SIL 3
60 % - < 90 %
SIL 2
SIL 3
SIL 4
90 % - < 99 %
SIL 3
SIL 4
SIL 4
≥ 99 %