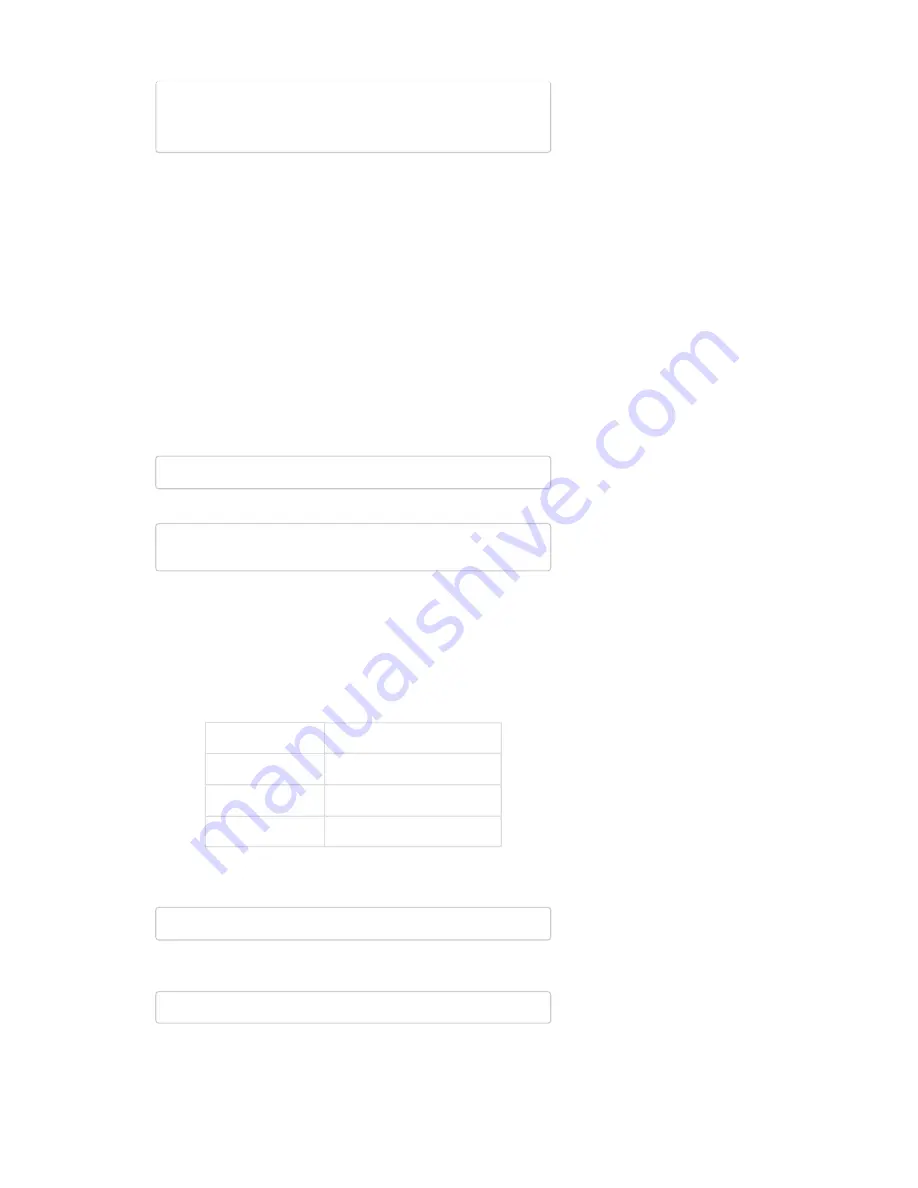
digitalWrite(PWMB,
LOW);
digitalWrite(DIRA,
LOW);
digitalWrite(DIRB,
LOW);
}
Then upload to your Arduino and watch your motors spin! If you want to dig
really deep into the sketch, check out the comments.
Explaining the Sketch
For each motor there are two mechanisms we can control — the
direction
of rotation and the
speed
. Each of those mechanisms is controlled by one
pin on the Arduino.
Controlling Rotation Direction
We can only spin the motor in two directions — clockwise or
counterclockwise — so we only need two values — 0 or 1 — to control that
from the Arduino. We can simply
digitalWrite
either of the direction pins
(pin 12 for motor A, pin 13 for motor B)
HIGH
or
LOW
to go forward or
backward.
For example, if you want motor A to spin clockwise, you simply need to
digitalWrite
pin 12
LOW
:
digitalWrite(12,
LOW);
//
Motor
A
will
spin
clockwise
To make it spin the other way, write the pin
HIGH
.
digitalWrite(12,
HIGH);
//
Motor
A
will
spin
counter
clockwis
e
(
Note:
The rotation direction depends on how you wired the motor to your
shield. If you swapped the red and black wires, the motor will spin opposite
of how we’ve described it here.)
Speeding
To control the speed of a motor we need to
analogWrite
to the PWM pins
(pin 3 for motor A, pin 11 for motor B). A higher
analogWrite
value means
a faster spin. Writing the pin
LOW
(or 0) will stop the motor.
PWM Value
Motor Spin Speed
0
Off (Stop)
127
Half Speed
255
Full Speed
If we want to turn motor A up to maximum speed, this is all we need:
analogWrite(3,
255);
//
Motor
A
at
max
speed
After that line of code is executed, the
motor will spin until stopped
. To
stop the motor, replace 255 with 0:
analogWrite(3,
0);
//
Stop
motor
A
Don’t forget to set your direction before spinning your motor!
Resources and Going Further
Page 14 of 17

















