Command List
VISCA Communication Specifications
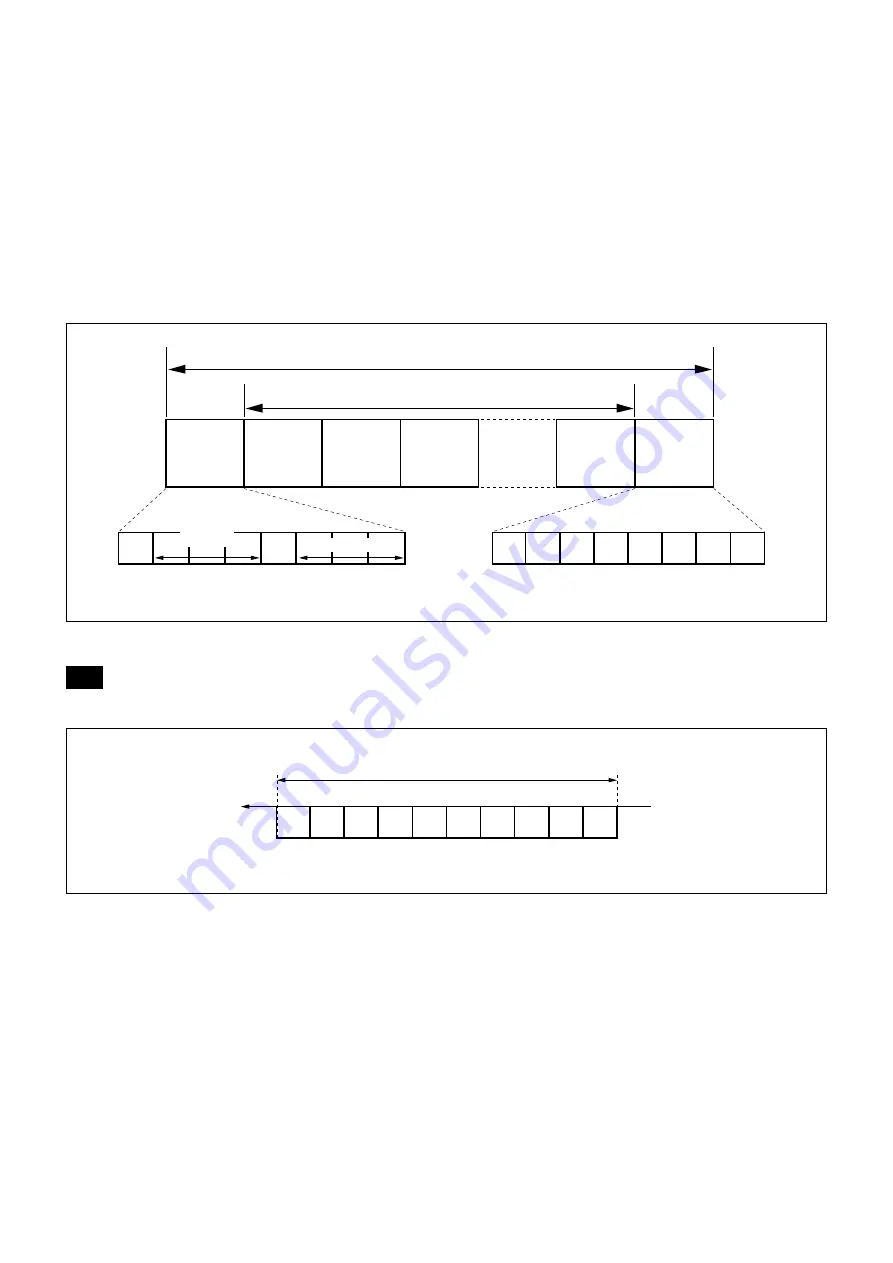
VISCA packet structure
The basic unit of VISCA communication is called a packet (Fig. 2). The first byte of the packet is called the header
and comprises the sender’s and receiver’s addresses. For example, the header of the packet sent to the SRG assigned
address 1 from the controller (address 0) is 81h in hexadecimal. The packet sent to the SRG assigned address 2 is
82h. In the command list, as the header is 8X, input the address of the SRG to X. The header of the reply packet
from the SRG assigned address 1 is 90h. The packet from the SRG assigned address 2 is A0h.
Some of the setting commands for SRG can be sent to all devices at one time (broadcast)*. In the case of broadcast,
the header should be 88h in hexadecimal.
When the terminator is FFh, it signifies the end of the packet.
* The broadcast function is not available for VISCA over IP.
Bit 7
(MSB)
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
(LSB)
1
0
FF
Bit 7
(MSB)
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
(LSB)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Header
Message (1 to 14 bytes)
Packet (3 to 16 bytes)
Terminator
Byte 1
Byte 3
Byte 2
Sender’s
address
Receiver’s address
Fig. 2 Packet structure
Note
Fig. 2 shows the packet structure, while Fig. 3 shows the actual waveform. Data flow will take place with the LSB first.
Bit 0 Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5
(LSB)
(MSB)
Bit 6 Bit 7
1 byte
Start
bit
Stop
bit.
Fig. 3 Actual waveform for 1 byte.
















































