3. Net-Log Set-up & Installation
Above this stream rate, play streaming will start to fail,
i.e. there will be non-continuous audio and audio silences
on playback.
E.g. 2 people play streaming 64kbps recording
= 2 x 64kbps = 128kbps, plus
2 people play streaming 384kbps recording
= 2 x 384kbps = 768kbps
Total = 896kbps, which is less than 900kbps and
allowable.
Play streaming can occur with archiving also happening in
the background. Archiving audio to a nominated hard-
drive on the network happens at a maximum data rate of
1000kbps. This data rate falls if play streaming is
occurring, because play streaming is given a priority over
any other process. There is a downside of this priority,
which is that if many people are play streaming
continuously for a number of hours (or days), the
archiving data rate may fall below the recording data rate,
so that the audio is not being archived as quickly as it is
recorded.
You can calculate whether this will happen by subtracting
the total maximum stream rate (calculated in the above
example) from 1000kbps. If the remainder is less than the
recording bit rate that you are archiving, then your
archiving may happen at less than real time and will,
eventually fail. Note: this does assume that the play
streaming is at, or beyond, the maximum for a
considerable length of time (to fill the Net-Log hard disk).
Invariably, the play streaming is for “dip-in” access of a
short duration (<1 hour) and the archive process has time
to catch-up when there is no, or little, play streaming.
Connecting Net-Log To Your
Network
Before connecting the Net-Log you first need to give it an
IP Address, Subnet Mask and a Default Gateway. You may
need to obtain these from your network administrator, but
please note that the Net-Log is not compatible with DHCP
(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) and DNS (Domain
Name System).
To help in your selection of an IP Address for the Net-Log,
following is a brief description of how IP Addresses and
Subnet Masks work.
IP Addresses
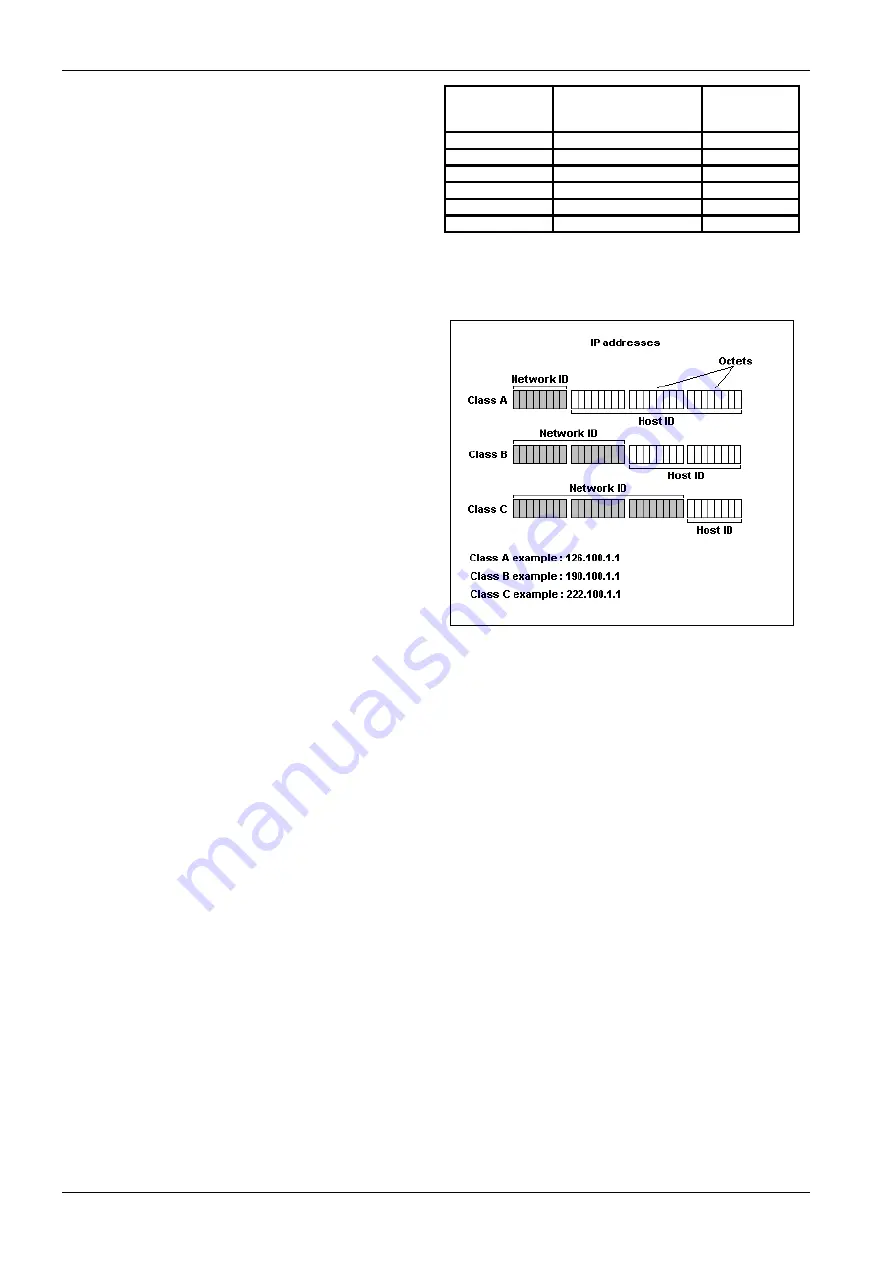
An IP Address is used to determine where a node (PC,
Printer etc.) is situated on a network. This address must
be unique to the network, otherwise conflicts will occur.
The actual address is made up of 32 bits, split into four
sections (each section is called an octet). Held in the
address is a network ID and host ID.
The network ID, or network address, is basically the
address of the local network, and all nodes within that
network must have the same network ID. The host ID part
of the address identifies the node within that network.
There are three different classes of IP Address: A, B and
C. These determine what parts of the address contain the
network ID and the host ID, (
Figure 3.3
).
Figure 3.2 Maximum Simultaneous Streams
Figure 3.3 IP Addresses
MPEG Record
Bit Rate
Maximum number
of simultaneous
streams
Total
stream rate
160 kbps
5 streams
800 kbps
192 kbps
4 streams
768 kbps
224 kbps
4 streams
896 kbps
256 kbps
3 streams
768 kbps
320 kbps
2 streams
640 kbps
384 kbps
2 streams
768 kbps
Sonifex Net-Log User Handbook
14
Summary of Contents for Net-Log
Page 1: ...Sonifex Net Log User Handbook...
Page 6: ...Contents Sonifex Net Log User Handbook...
Page 10: ...License Form Sonifex Net Log User Handbook 4...
Page 16: ...1 Introduction Sonifex Net Log User Handbook 10...
Page 24: ...3 Net Log Set up Installation Sonifex Net Log User Handbook 18...
Page 32: ...5 Recording Sonifex Net Log User Handbook 26...
Page 36: ...6 Playing Downloading Sonifex Net Log Win User Handbook 18...
Page 48: ...9 Serial Control Interface Sonifex Net Log Win User Handbook 30...
Page 56: ...11 The Administrator Sonifex Net Log Win User Handbook 38...
Page 62: ...13 Technical Specification Sonifex Net Log Win User Handbook 44...
Page 64: ...14 Glossary Sonifex Net Log Win User Handbook 46...