User Manual - twentynine
4.1
CMOS Sensor Readout
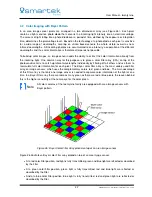
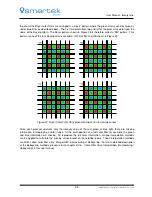
A CMOS sensor reads the accumulated charge of each cell in the image individually, where it was already
converted to a voltage. There are several transistors at each pixel which do the conversion and make each
pixel be addressable by the horizontal and vertical circuit, using more traditional wires. Because of the high
demand for space by additional transistors on each pixel, the light sensitivity of a CMOS chip tends to be
lower, as the photosensitive area shrinks with the amount of transistors.
Each pixel is read out and reset separately after each other. On Global Shutter CMOS sensors the charge
of each pixel is additionally buffered in a non-photosensitive area of the pixel before, while on Rolling Shutter
sensors the charge is read out directly from the exposed pixel. This postpones the moment of readout and
thus shifts (Electronic Rolling Shutter) or extends (Global Reset Release) the duration of exposure from
pixel to pixel (and line to line). Both architectures have their advantages and disadvantages; while a Rolling
Shutter has problems in motion scenes due to the fact that the lower lines of the images are later exposed
than the top ones, Global Shutter sensors show up additional noise and lower sensitivity due to their higher
amount of transistors per pixel. In case of a Rolling Shutter the mentioned effect can be removed by using
strong synchronized strobe illuminations or a mechanical shutter.
B
ias Gen
er
a
tion
Cl
o
ck &
Timing
Genera
tio
n
ADC
Oscillat
or
FPGA
Image Sensor (CMOS APS)
Light sens
iti
ve pixel
Pixel t
o
be transferred
V
erti
cal
Sc
a
n
C
ir
cu
it
H
o
riz
o
ntal Scan Circuit
C
o
lumn Amps
Camera Frontend
B
ias De
c
ou
p
ling
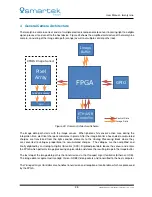
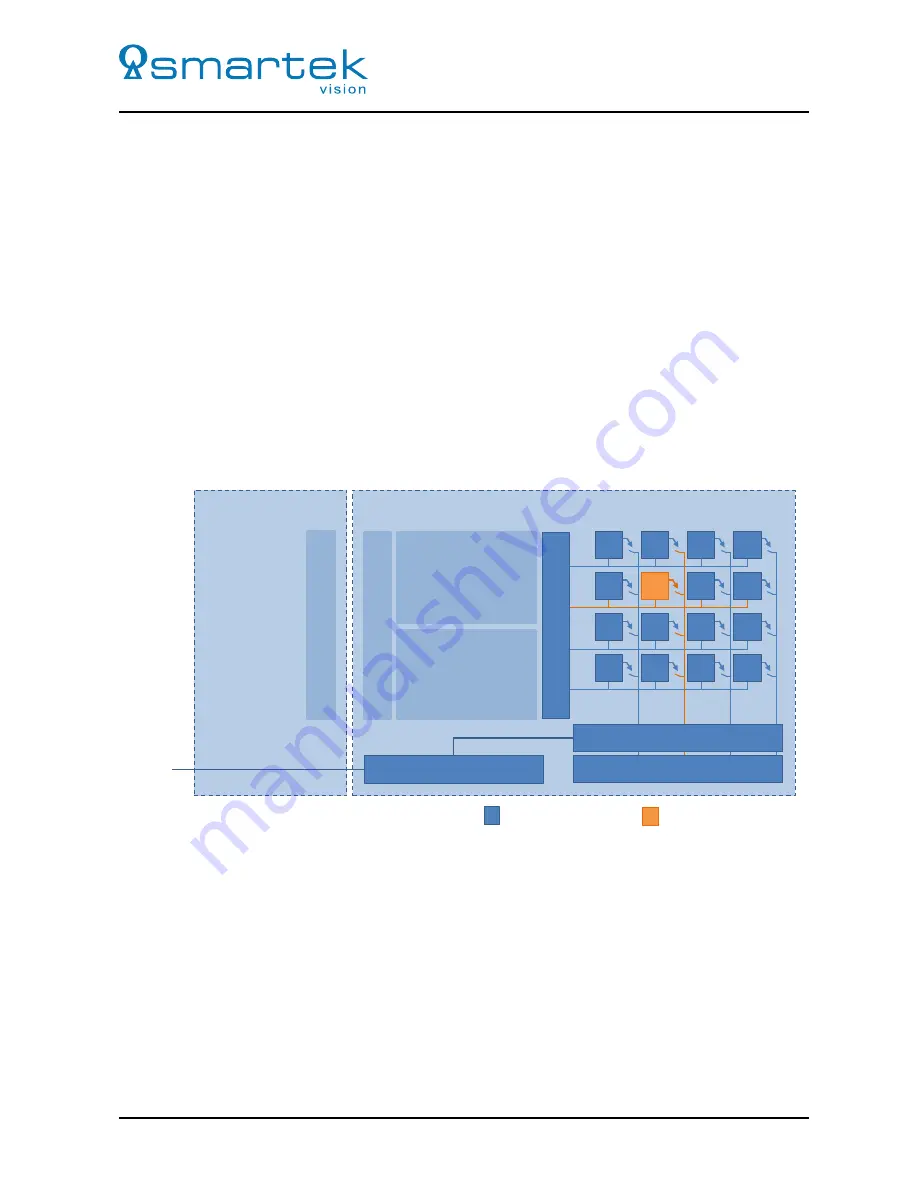
Figure 25: twentynine Frontend with CMOS Active Pixel Sensor with integrated Gain and ADC
As shown in Figure 25, on CMOS image sensors the image data is already amplified in the sensor’s
Column
Amps
and digitized by the
ADC
before leaving the image sensor. Depending on the sensor type, also
additional processing can already take place within the sensor. The output of the CMOS image sensors used
is a digital signal which can directly be forwarded to the camera’s FPGA. The electronics in the camera’s
frontend are mainly dedicated to provide clean and separated supply powers for the sensor and its periphery,
and route the sensor control bus (I
2
C / SPI).
36
SMARTEK Vision | User Manual - twentynine | Doc. v1.0.2