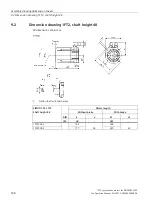
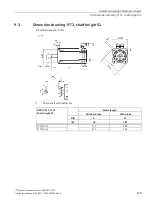
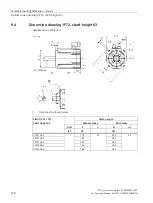
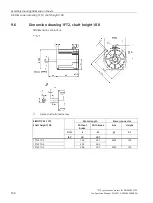
Glossary
1FT2 synchronous motors for SINAMICS S120
136
Configuration Manual, 03/2021, A5E50645584B AA
NDE
Non-drive end = Non-drive end of the motor
Static torque M
0
Thermal torque limit when the motor is at a standstill corresponding to the motor thermal
class. M
0
is always
≥
the rated torque M
N
.
Stall current I
0
Motor phase current to generate the particular static torque (M
0
= k
T
• I
0
). Specification of the
RMS value of a sinusoidal current.
Thermal time constant T
th
Defines the increase in the motor frame temperature when the motor load is suddenly
increased (step function) to the permissible S1 torque. The motor has reached 63% of its final
temperature after T
th
.
Moment of inertia J
Mot
Moment of inertia of rotating motor parts. J
Mot
= without brake, J
Mot Br
= with brake.