RUGGEDCOM RUGGEDCOM RS940G
Installation Guide
Chapter 2
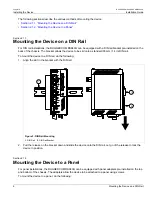
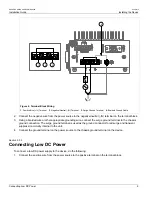
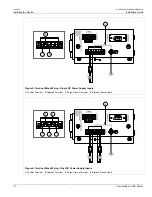
Installing the Device
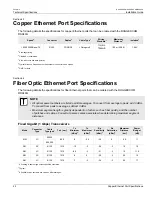
Gigabit Ethernet 1000Base-TX Cabling
Recommendations
13
Siemens also does not recommend using copper Ethernet ports to interface with devices in the field across
distances that could produce high levels of ground potential rise (i.e. greater than 2500 V), during line-to-ground
fault conditions.
Section 2.5.2
Gigabit Ethernet 1000Base-TX Cabling Recommendations
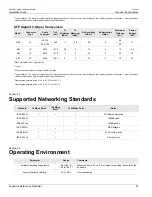
The IEEE 802.3ab Gigabit Ethernet standard defines 1000 Mbit/s Ethernet communications over distances of up
to 100 m (328 ft) using all 4 pairs in category 5 (or higher) balanced, unshielded twisted-pair cabling. For wiring
guidelines, system designers and integrators should refer to the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA)
TIA/EIA-568-A wiring standard that characterizes minimum cabling performance specifications required for proper
Gigabit Ethernet operation. For reliable, error-free data communication, new and pre-existing communication
paths should be verified for TIA/EIA-568-A compliance.
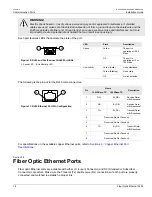
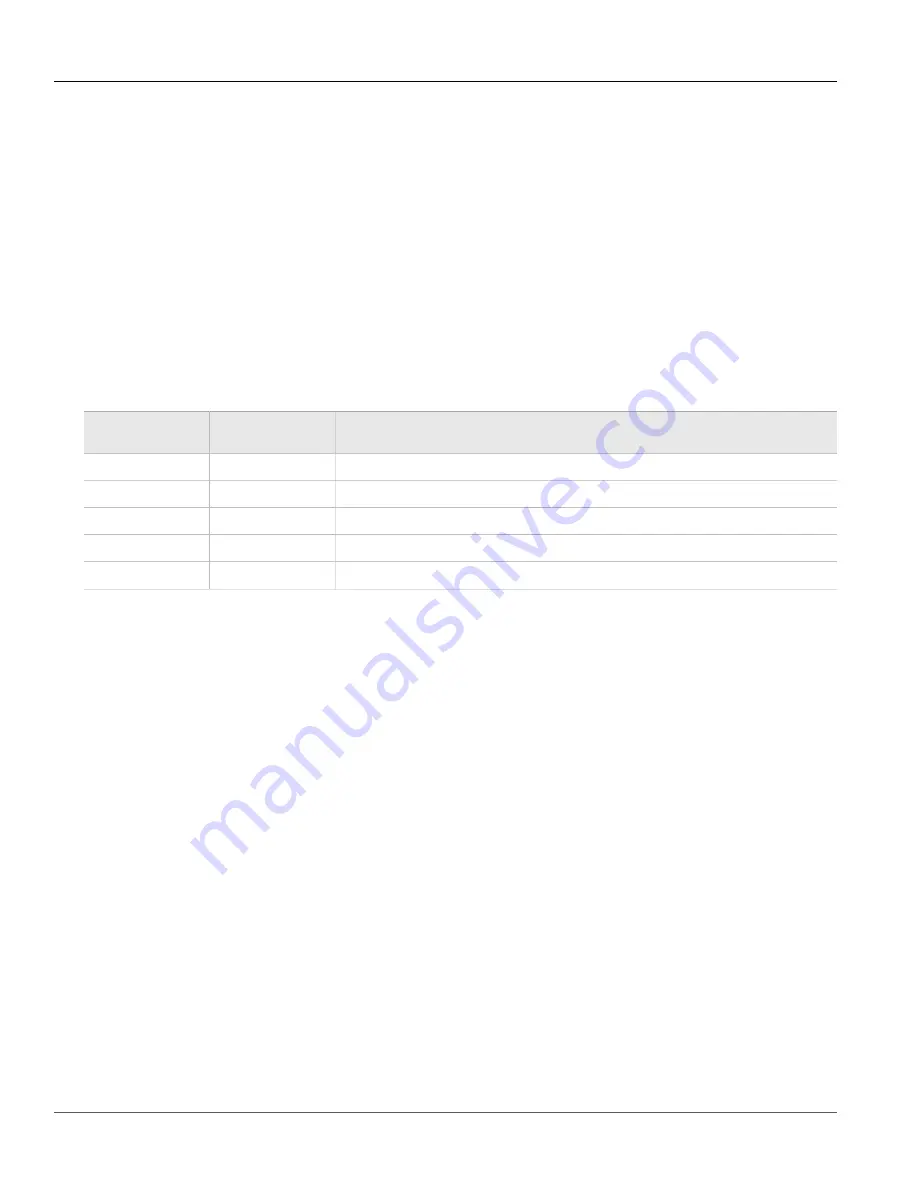
The following table summarizes the relevant cabling standards:
Cabling Category
1000Base-
TX Compliant
Required Action
< 5
No
New wiring infrastructure required.
5
Yes
Verify TIA/EIA-568-A compliance.
5e
Yes
No action required. New installations should be designed with Category 5e or higher.
6
Yes
No action required.
> 6
Yes
Connector and wiring standards to be determined.
Follow these recommendations for copper data cabling in high electrical noise environments:
• Data cable lengths should be as short as possible, preferably 3 m (10 ft) in length. Copper data cables should
not be used for inter-building communications.
• Power and data cables should not be run in parallel for long distances, and should be installed in separate
conduits. Power and data cables should intersect at 90° angles when necessary to reduce inductive coupling.
• Shielded/screened cabling can be used when required. Care should be taken to avoid the creation of ground
loops with shielded cabling.