18 - EN
•
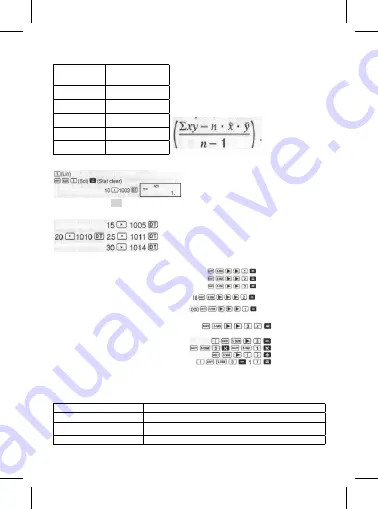
Example
: Atmospheric Pressure vs. Temperature
Temperature
Atmospheric
Pressure
Perform linear regression to determine the regression
formula terms and correlation coefficient for the data
nearby. Next, use the regression formula to estimate
atmospheric pressure at 18°C and temperature
at 1000 hPa. Finally, calculate the coefficient of
determination
(r
2
)
and sample covariance
10
°
1003 hPa
15
°
1005 hPa
20
°
1010 hPa
25
°
1011 hPa
30
°
1014 hPa
In the REG Mode:
Each time you press DT to register you input, the number of data input up to that point is
indicated on the display (
n
value)
Registration Coefficient
A =
997.4
Registration Coefficient
B = 0.56
Correlation Coefficient
r = 0.982607368
Atmosphere Pressure at 18°C =
1007.48
Temperature at 1000 hPa =
4.642857143
Coefficient of Determination =
0.955517241
Sample Covariance =
35
•
Logarithmic, Exponential, Power, and Inverse Regression
•
Use the same key operations as linear regression to recall results for these types of regression.
•
The following shows the regression formulas to reach type of regression
Logarithmic Regression
y = A + B . ln x
Exponential Regression
y = A . e
B
⋅
x
(ln y = ln A + Bx)
Power Regression
y = A . x
B
(ln y = ln A + B in x)
Inverse Regression
y = A + B .
1
/x
© FAST ČR a. s.
Summary of Contents for SEC 102
Page 1: ......
Page 2: ...FAST R a s...








































