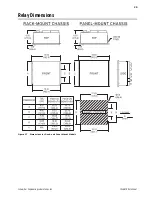
SEL-487B Data Sheet
Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc.
12
Time Synchronization, Automation, and Communication
Time Synchronization
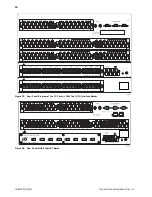
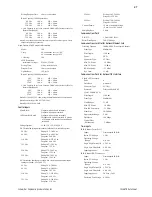
To synchronize the relays in a three-relay application,
use the unique
IN
and
OUT
IRIG-B connectors installed on
each relay for the IRIG-B signal. Referring to the
External Source connections in Figure 20, connect the
IRIG-B signal to the
IN
connector of Relay A to update
the time. Connect the
OUT
connector of Relay A to the IN
connector of Relay B to update the time in Relay B. Use
a similar connection between Relay B and Relay C to
update the time in Relay C. In the absence of an external
IRIG-B signal, connect the relays as shown by the
Internal Source connections in Figure 20. Connected this
way, Relay B and Relay C synchronize to the internal
clock of Relay A. The event reports the different relays
generate are time-stamped to within 10 µs of each other.
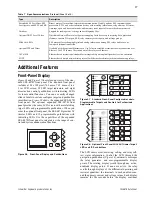
Figure 20
Time Synchronize SEL-487B Relays With or
Without External Clock Source
Precision Time Protocol (PTP)
Time Synchronization
In addition to IRIG-B, the relay can be time synchro-
nized through the Ethernet network using IEEE 1588
Precision Time Protocol, version 2 (PTPv2). When con-
nected directly to a grandmaster clock providing PTP at
1-second sync intervals, the relay can be synchronized to
an accuracy of ±100 ns. The relay is capable of receiving
as many as 32 sync messages per second.
Figure 21
Example PTP Network
SNTP Time Synchronization
Use simple network time protocol (SNTP) to cost-
effectively synchronize SEL-487B relays equipped with
Ethernet communication to within ±1 ms with no time
source delay. Use SNTP as a primary time source, or as a
backup to a higher accuracy IRIG-B time input to the
relay.
Figure 22
SNTP Diagram
Automation
Time-Domain Link (TiDL) Technology
The SEL-487B supports remote data acquisition through
use of an Axion with a technology known as TiDL. The
Axion provides remote analog and digital data over an
IEC 61158 EtherCAT TiDL network. This technology
provides very low and deterministic 1.5 ms latency over
a point-to-point architecture. The SEL-487B Relay can
receive as many as eight fiber links from as many as eight
Axion remote data acquisition nodes.
The relay supports a number of fixed topologies. The
relay maps the voltage and current inputs from the Axion
to existing analog quantities in the SEL-487B Relay
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
SEL-487B
SEL-487B
SEL-487B
SEL-487B
SEL-487B
SEL-487B
Relay A
Relay A
Relay B
Relay B
Relay C
Relay C
IRIG-B
Clock Receiver
External Source
Internal Source
IRIG-B
IRIG-B
SEL-487B
SEL-487E
SEL-411L
SEL-421
SEL-451
GPS
SEL-2488
SEL-2740M
SEL-487E SEL-487E SEL-487E SEL-487E
SEL-3354
SEL-2725
SEL-2401