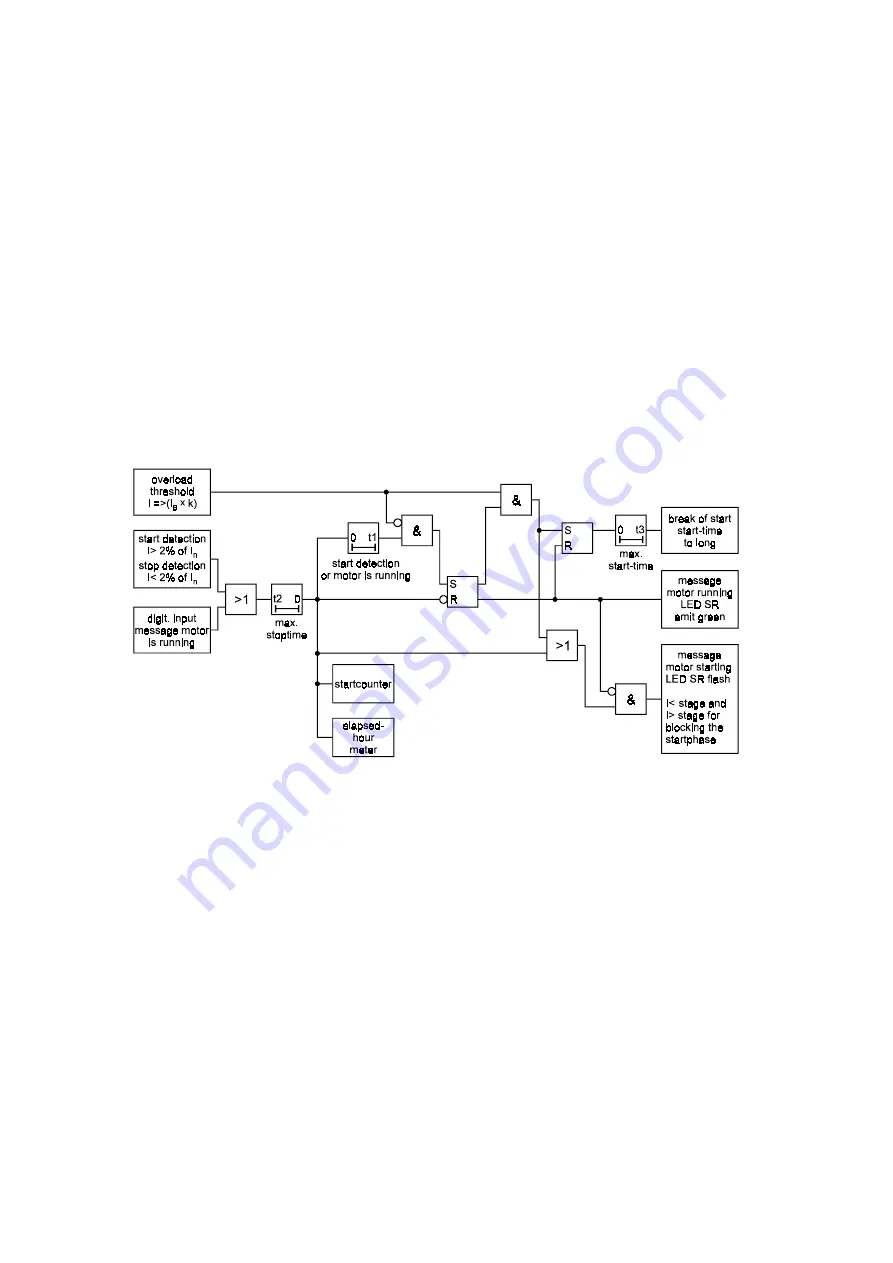
10
TB MRM3 07.01 E
•
No exeeding of the start threshold during pony mo-
tor start-up or when soft starters are used.
•
Multistage resistance start where the start threshold is
either exceeded several times or not at all.
The time is running from the instance the start threshold
is exceeded. RUNNING is only accepted by the su-
pervision after the time has elapsed or the overload
threshold is undershot. If the overload threshold is not a
clear criterion, the time has to be set at least for so
long that the longest regular start procedure is cov-
ered.
RUNNING can be recognised in different ways:
•
If the START has been successfully completed. This
is the case when the motor current has dropped
below k x IB and the start recognition time has
elapsed. (direct start)
or
•
if the motor is connected across several resistance
steps, it is possible that the start threshold is
passed through repeatedly. RUNNING conditions
are recognised when the start recognition time has
run out after the last step and a current has settled
between 2% IN and k x IB t.
(Resistance start).
•
if after STOP a motor current has settled between
2% IN and k x IB and the start recognition time
has elapsed. The overload threshold has not nec-
essarily to be exceeded.
(soft start)
•
If the «Motor Running» input was activated but the
overload threshold is not (or not any longer) ex-
ceeded. (See Chapter 5.12.3 )
With the recognition of STOP, the RUNNING condi-
tions have ceased to exist.
Figure 4.2: Flow Diagram of the Start Conditions
4.1.1 Criteria for Blocking the Start
Number of monitored starts :
The
MRM3
is equipped with a flexible supervision
element which can limit the sequence of possible
starts.
A start should be prevented if it is obvious that it is
likely to be interrupted due to overload so that in total
the down-time can be curtailed. If a start is not rec-
ommendable at a certain time (with the motor
switched off), the
MRM3
activates an allocated output
relay until the waiting time has elapsed. Irrespectively
of the adjustment of this element, the thermal image is
always activated and shuts the motor down as soon as
the thermal overload threshold is reached (due to a
start or overload).
The protective element can either be tied to the thermal
image or be manually defined by the number of starts
and cycle duration.











































