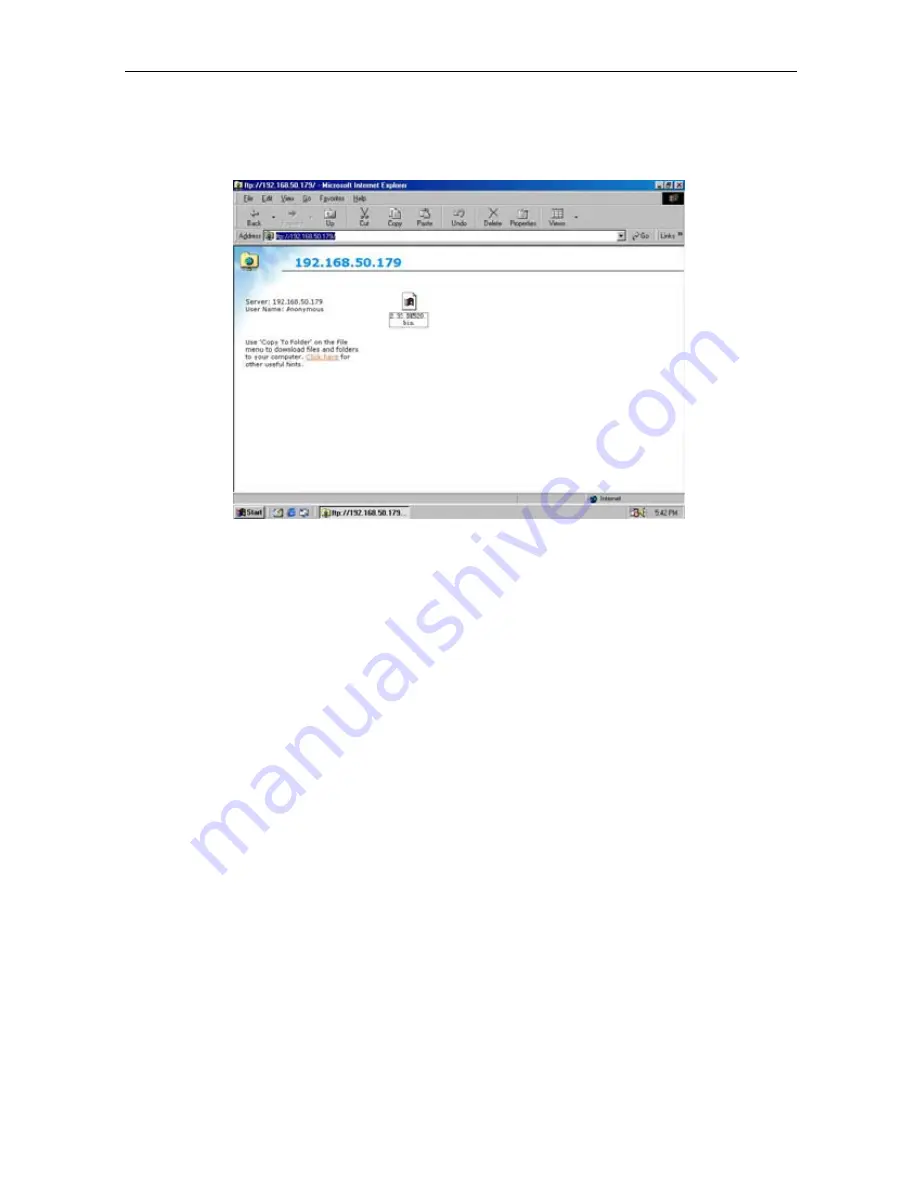
Once the connection has been established, the following window will be displayed.
The user may then transfer the latest firmware here in order to complete the
updating steps.
Appendix C: IP Address, Subnet and Gateway
This section discusses Communities, Gateways, IP Addresses and Subnet masking
Communities
A community is a string of printable ASCII characters that identifies a user group with the
same access privileges. For example, a common community name is “public.”
For security purposes, the SNMP agent validates requests before responding.
The
agent can be configured so that only trap managers that are members of a community
can send requests and receive responses from a particular community.
This prevents
unauthorized managers from viewing or changing the configuration of a device.
Gateways
Gateway, also referred to as a router, and is any computer with two or more network
adapters connecting to different physical networks. Gateways allow for transmission of
IP packets among networks on an Internet.
IP Addresses
Every device on an Internet must be assigned a unique IP (Internet Protocol) address.
An IP address is a 32-bit value comprised of a network ID and a host ID.
The network
ID identifies the logical network to which a particular device belongs.
The host ID
identifies the particular device within the logical network.
IP addresses distinguish
devices on an Internet from one another so that IP packets are properly transmitted.
IP addresses appear in dotted decimal (rather than in binary) notation.
Dotted decimal
notation divides the 32-bit value into four 8-bit groups, or octets, and separates each
octet with a period. For example, 199.217.132.1 is an IP address in dotted decimal
notation.
To accommodate networks of different sizes, the IP address has three divisions –
Classes A for large, B for medium and C for small.
The difference among the network
classes is the number of octets reserved for the network ID and the number of octets
IP Camera Manual
61