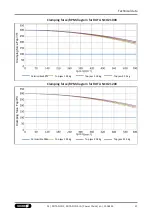
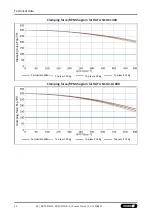
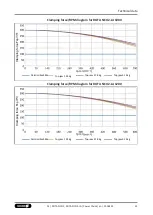
Technical data
(–)
for gripping from the outside inwards
(+)
for gripping from the inside outwards
DANGER
Risk to life and limb of the operating personnel and significant
property damage when the RPM limit is exceeded! With
gripping from the outside inwards, and with increasing RPM,
the effective clamping force is reduced by the magnitude of the
increasing centrifugal force (the forces are opposed). When the
RPM limit is exceeded, the clamping force drops below the
required minimum clamping force F
spmin
. Consequently, the
workpiece is released spontaneously.
•
Do not exceed the calculated RPM.
•
Do not fall below the necessary minimum clamping force.
The workpiece
will be
uncontrollably
released in
this area
Speed of rotation
Clamping force
Centrifugal
force
Effective clamping force
Minimum required clamping force
Initial clamping force during shutdown
Reduction in effective clamping force by the magnitude of the total centrifugal force, for gripping from the outside
inwards.
The required effective clamping force for machining F
sp
is
calculated from the product of the
machining force F
spZ
and the
safety factor S
z
. This factor takes into account uncertainties in the
calculation of the machining force. According to VDI 3106:
S
z
≥ 1.5.
From this we can derive the calculation of the initial clamping
force during shutdown:
(+)
for gripping from the outside inwards
(–)
for gripping from the inside outwards
25
01 | ROTA NCO2, ROTA NCO2-JA | Power Chuck | en | 1506425