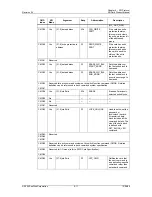
Chapter 5 – SPI Protocol
Revision 2.2
SD Card Product Manual
© 2004 SanDisk Corporation
5-2
12/08/04
5.3
Bus Transfer Protection
CRC bits protect every SD Card token transferred on the bus. In SPI mode, the SD Card
offers a non protected mode which enables systems built with reliable data links to exclude
the hardware or firmware required for implementing the CRC generation and verification
functions.
In the non-protected mode the CRC bits of the command, response and data tokens are still
required in the tokens however, they are defined as “don’t care” for the transmitters and
ignored by the receivers.
The SPI interface is initialized in the non-protected mode. The host can turn this option on
and off using CRC_ON_OFF command (CMD59).
The CRC7/CRC16 polynomials are identical to that used in SD Bus mode. Refer to this
section in the SD Bus mode chapter.
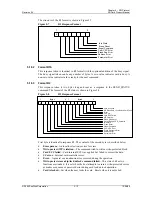
5.4 Data
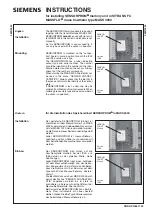
Read
SPI mode supports single block and multiple-block read operations (SD Card CMD17 or
CMD18). Upon reception of a valid read command the card will respond with a response
token followed by a data token in the length defined in a previous SET_BLOCK_LENGTH
(CMD16) command (see Figure 5-1).
Figure 5-1
Single Block Read Operation
A valid data block is suffixed with a 16-bit CRC generated by the standard CCITT
polynomial: x
16
+x12+x
5
+1.
The maximum block length is 512 bytes as defined by READ_BL_LEN (CSD parameter).
Block lengths can be any number between 1 and READ_BL_LEN.
The start address can be any byte address in the valid address range of the card. Every
block, however, must be contained in a single physical card sector.
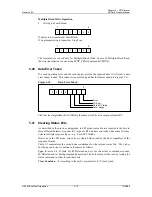
In case of data retrieval error, the card will not transmit any data. Instead, a special data
error token will be sent to the host. Figure 5-2 shows a data read operation, which
terminated with an error token rather than a data block.
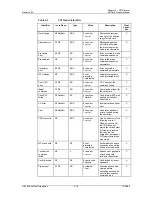
Command
DataIn
Command
Response
Data Block
CRC
From Host
to Card
From Card
to Host
Data from
Card to Host
Next Command
DataOut