1011-540 5-17-04
Operation
19
S&C Electric Company
BankGuard PLUS
Proprietary Information
Control
voltage magnitude. Therefore, the compensated neutral-to-ground voltage will also
change. If the compensated neutral-to-ground voltage magnitude exceeds a setpoint value,
then the appropriate control action will be taken.
Figure 8
Corrected Magnitude
•
For a grounded wye capacitor bank installation with the Unbalance Compensation
feature disabled, the Discrete Fourier Transform algorithm yields the magnitude of the
sum of the tap-point-to-ground voltages (in percent). Capacitor unit failures will cause a
change to the magnitude of the real-time sum of the tap-point-to-ground voltages. If the
magnitude of the sum of the tap-point-to-ground voltages exceeds a setpoint value(s), then
the appropriate control action will be taken.
•
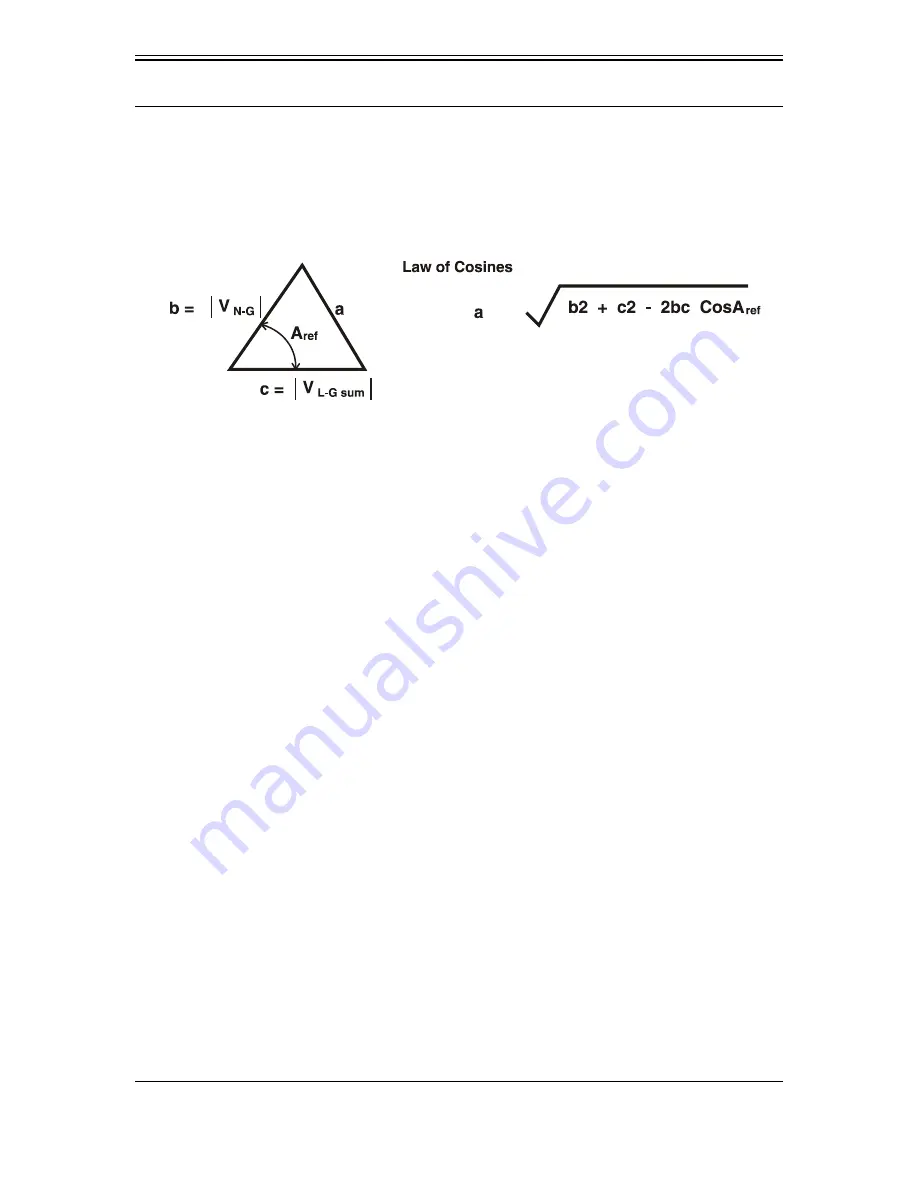
For a grounded wye capacitor bank with the Unbalance Compensation feature set to
“Enable”, the Discrete Fourier Transform algorithm yields the magnitude of the sum of
the intermediate tap-point voltages (|V tap sum|) and the value of the phase angle (A
ref
)
between the tap-point voltages sum and the reference line voltage. Using the Law of
Cosines, an approximate corrected magnitude is obtained utilizing the reference angle
(See Figure 4-6). An approximate corrected magnitude is calculated and stored in the
control’s memory during the feature’s setup procedure. When the control is operating, the
stored, approximate corrected magnitude is subtracted from the real-time tap-point-to-
ground voltages magnitude (in percent) during each 200 milliseconds to obtain a
compensated neutral-to-ground voltage magnitude. The compensated neutral-to-ground
voltage magnitude is then compared to the setpoint value(s). The calculation on the
compensated neutral-to-ground voltage value is the same as for an ungrounded, wye-
connected shunt capacitor bank. Capacitor unit failures will cause a change to the
magnitude of the real-time tap-point-to-ground voltages sum and the reference angle.
Therefore, the magnitude of the compensated neutral to ground voltages sum magnitude
will also change. If the magnitude of the compensated tap-point-to-ground voltages sum
magnitude exceeds a setpoint value, the appropriate control action will then be taken.










































