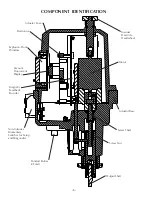
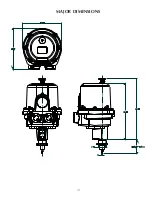
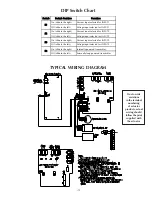
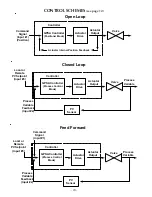
-10-
ACTUATOR SETUP
General
1) Power
Unit automatically senses 100 to 240 Vac input power.
2) Command Calibration
Unit is factory calibrated for input commands of both 4-20ma
and 1-5 Volts. There is no need for the customer calibration
of the input signals.
3) Auto/Manual
The unit can be operated in Manual or Automatic modes.
See the Menu Hierarchy for the location of this user settable
selection.
4) Calibration
The unit may be calibrated in one of two modes (Zero/Span
or Characterize)
Interface
A display and two selector knobs are used for a non-intrusive
customer interface to the actuator. The unit provides a
menuing system to access run modes, parameters,
diagnostics and alarms. The
↑
and
↓
selections are used to
scroll through the menu choices and status/parameter lists.
These parameters are arranged in a tree structure which is
traversed using the
↑
and
↓
knob selections.
Selecting the
↓
option will scroll down one entry in the
parameter listing. The next parameter will be shown on the
top line of the display. Selecting
↑
will scroll back up to the
previous parameter in the list. Each menu listing is circular.
The menu listings contain parameters and access to
additional menus of parameters. Menus are distinguished by
using only the top line of the display. When a menu is
shown, selecting
E
nter takes the operator to that menu and
again the
↑
/
↓
selections are used to traverse it.
C
ancel
moves back to the previous menu.
Parameters use both display lines. A parameter’s name is
shown on the top line and its current value is shown on the
bottom line. When a parameter is shown (if it is updateable),
selecting
E
nter will put that parameter in the update mode.
This is denoted by a “U” in the upper left hand corner of the
display. The
↑
/
↓
selections are now used to modify the
parameter value. If the parameter has discrete settings,
↑
/
↓
will cycle through the circular list of those settings. If the
parameter is numeric, the
↑
/
↓
knob selections will
increment or decrement the parameter respectively.
When updating a numeric parameter value, holding a knob
selection (
↑
or
↓
) will increase the amount of increment (
↑
)
or decrement (
↓
)
in use. Initially a parameter is updated
through its least significant digit. Holding the knob selection
through ten changes will advance the update one position to
the left for an additional ten updates. This process continues
until the knob is released. All numeric parameters have
minimum and maximum limits. The update of parameters is
circular. For example, incrementing a parameter past its
maximum value will cause the value to loop around to its
minimum value and continue updating from that point.
Updating a parameter causes the unit to enter Manual Mode.
The unit will remain in Manual Mode until the operator
returns it to Automatic mode via the “AUTO/MAN CTRL”
parameter.
Zero/Span
– This option provides a 2-point calibration of the
unit. This calibration is performed under the VALVE POS
menu via the following steps:
1. Update the MAX POSITION parameter to reflect the
value of the maximum output position of the actuator.
(ex. 100 %)
2. Select the CAL POINT 1 parameter. Use the
↑
/
↓
knob
to run the actuator to the desired ZERO position. Select
E
nter to save the current physical position of actuator as
its ZERO point.
3. Continue to the CAL PT 1 VAL parameter and select it for
update. This is the numeric value that is to be associated
with the ZERO point (ex. 0 %). Update and select
E
nter
to save this value
4. Continue to the CAL POINT 2 parameter. Use the
↑
/
↓
knob to run the actuator to the desired SPAN position.
Select
E
nter to save the current physical position of
actuator as its SPAN point.
5. Continue to the CAL PT 2 VAL parameter and note that it
is automatically set to the MAX POSITION setting of step
1. This is the numeric value that is associated with the
SPAN point (ex 100 %). In a two-point calibration this
value is not updateable by the user.
6. The two-point calibration of the actuator is now
completed.
Cancel
Enter
Up
Down