LMA8 Mic/Line Preamplifier
4
Operational description
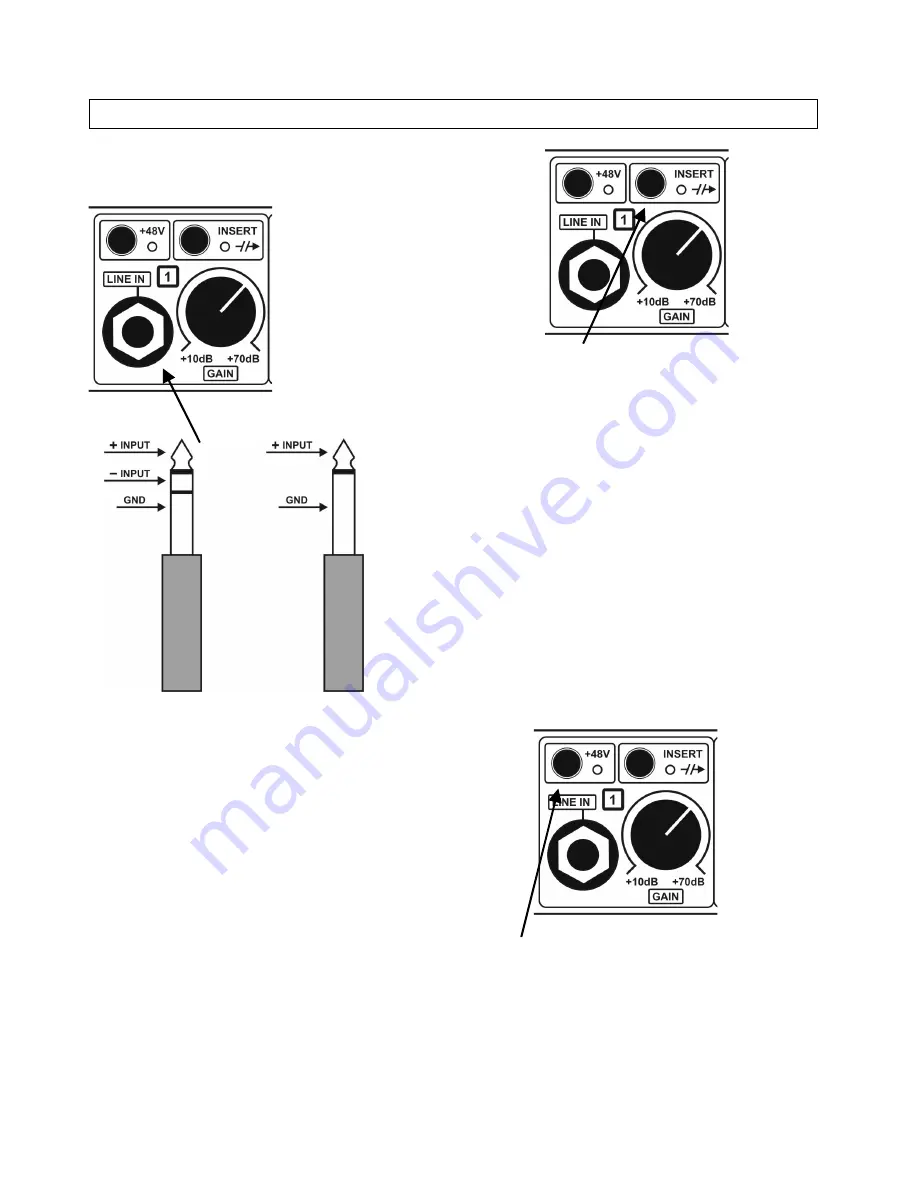
Instrument/line input
Each channel has a ¼" Jack instrument/line input on the
front panel. The input is for use with instruments (like
guitar, bass etc) and it can be used in a balanced as well
as an unbalanced configuration.
When a Jack is plugged-in, the input circuit automatically
disconnects the mic input, switches to high impedance
mode and activates the line input.
Plugging in a mono Jack enables the normal unbalanced
input configuration.
Plugging in a stereo Jack enables the balanced input
configuration.
For further information about using the balanced
configuration see page 8, Remote ground connection
Insert point switch
The toggle switch controls the bypass function of the
insert point. The insert point exists electrically between
the output of the preamp and the input of the digital
module.
When the LED is ON, the signal chain between the
preamp and the digital module is “open” which means
that external equipment can then be inserted between
line output/insert send and the insert return/direct input.
When the LED is OFF, the signal is routed directly from
the preamp to the digital module. The insert return/direct
input is then inactive.
The line output/insert send is not affected, and is always
active
When no digital module is installed, the switch has no
function. Pressing the switch will momentarily turn the
LED on, but the LED will automatically turn off again
after 2 seconds.
+48V Phantom Voltage
The toggle switch turns the Phantom Voltage at the mic
input on and off. The LED indicates the status.




















