45
Put a thin paper strip (no more than 80g paper!) between the motor pinion and the main pinion. Then manually turn
the main pinion so that the paper strip is pulled in between the two pinions.
The pressure of the paper pushes back the electric motor by the required measure.
Now tighten the motor‘s attachment screws again in this position.
If you then turn back the main cogwheel so that the paper strip can be removed again, both cogwheels should have
the correct distance.
Ideally, the motor pinion should be as close as possible to the main pinion without the teeth touching and the
gears therefore being tight.
If the cogwheels (motor pinion and main cogwheel) are too far apart, the main cogwheel teeth will be virtually
shaved off by the motor pinion after a few seconds - this will void the warranty/guarantee!
If the motor pinion presses against the main cogwheel (teeth are running without play), this will decrease
performance, increase power consumption (the motor already requires lots of power to turn the main gear)
and lead to premature wear.
d) Wheel Change
The tyres are fastened to the wheel rim to prevent them from coming loose. When the tyre is worn down, the entire
wheel has to be replaced therefore.
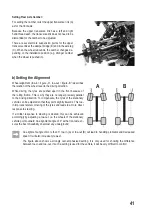
After loosening of the wheel nut (C), the wheel may be removed from the wheel axle.
Then the new wheel is plugged on so that the hexagon socket on the wheel rim‘s inside is precisely pushed onto the
hexagon of the brake disc dummy (B).
Screw the wheel onto the wheel axle (D) with the wheel nut (C) removed at first. However, do not apply any force for
screwing on. This will require greater force to turn the wheel, which may damage the drive.
The wheel tappet nut (A) with the brake disc dummy (B) may remain in the rim when removing the wheel or detach
from the wheel axle (D) when the wheel is taken off. In this case ensure that the driving pin (E) does not fall out and
get lost.
When the wheel is later replaced, ensure that the tappet pin (E) is exactly in the centre of the wheel axle (D) and
inserted into the respective groove of the wheel tappet nut (A).
If the tappet pin (E) is missing, no torque can be transferred from the motor to the wheel and the wheel will spin
freely.
A
B
C
D
A
B
C
D
E
E
Front axle
Rear axle