Rx-URME-007 Rev - -2
- Preliminary -
PMC665 Hardware Reference and Installation Manual
Page 6
3
PMC665 Architecture
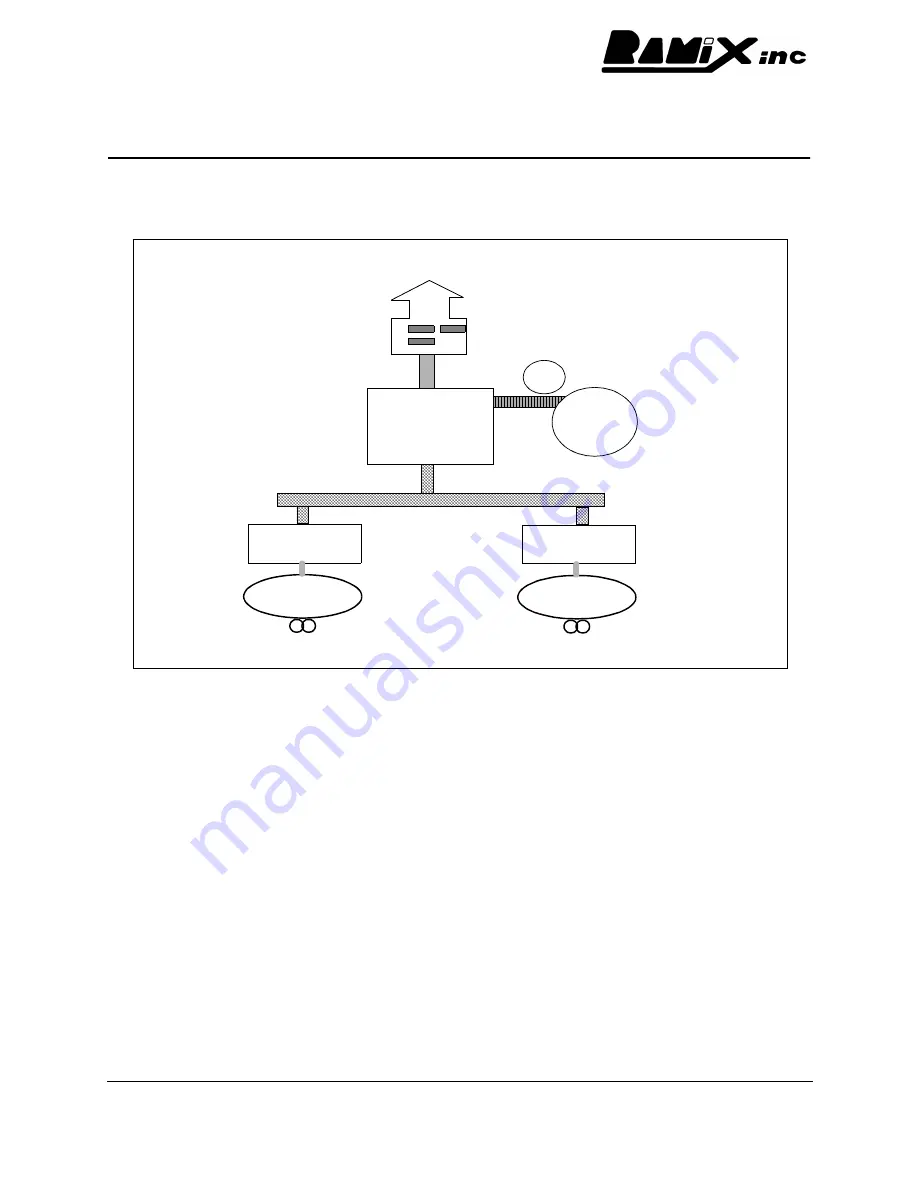
The PMC665 is a complete I/O subsystem, illustrated in the block diagram below:
3.0.1
PMC665 Subsystems
At the functional center of the PMC665 is the integrated bridge/Co-processor unit. Combining the
bridge and co-processor creates a high bandwidth, low latency integration between the
computational capabilities of the co-processor and the data flow of the bridge.
3.0.2
Transaction Isolation
There are three, independent busses contained on the PMC665: Host PCI bus, Secondary PCI
bus and Local co-processor bus. Data can flow between any pair; transactions have no affect on
traffic on the third bus. Thus, control and data flow between the Co-processor and local memory
system will consume no bandwidth on the Host PCI. It is this isolation that allows the PMC665 to
perform arbitrary manipulation, filter, etc., of data from the Ethernet, without compromising the
host system performance. The Co-processor/Bridge controller contains DMA engines, with FIFO
buffers to each of the busses. This is a critical factor, as the actual (opposed to theoretical)
bandwidth of a PCI bus decreases dramatically without burst (and relatively long burst) transfers.
3.0.3
Co-processor
The co-processor is an Intel i960 RISC CPU. The i960 architecture excels at data movement and
control, exactly the requirements of an I/O co-processor. Highly integrated, the i960 conforms
quite closely to the generic RISC architecture definition: single cycle instruction execution, multiple
Host PCI
100Mbit
MAC
Local PCI Bus
PCI/PCI
DRAM
Buffer &
Firmware
Boot
FLASH
Bridge
Fiber
Transceiver
100Mbit
MAC
Fiber
Transceiver
Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation ... Guaranteed | (888) 88-SOURCE | www.artisantg.com












