ProWi-Fi CEILING ACCESS POINTS
(Advanced Instructions)
Video tutorials are also available online on our
channel Blake UK Ltd
LAN & WAN information:- Shows current status of how the AP is
connected to WAN or LAN
2G and 5G Wi-Fi:- showing channel allocated .
Flow:- Shows upstream and downstream of current connections.
On the left side is the navigation buttons to other setup areas, as detailed below.
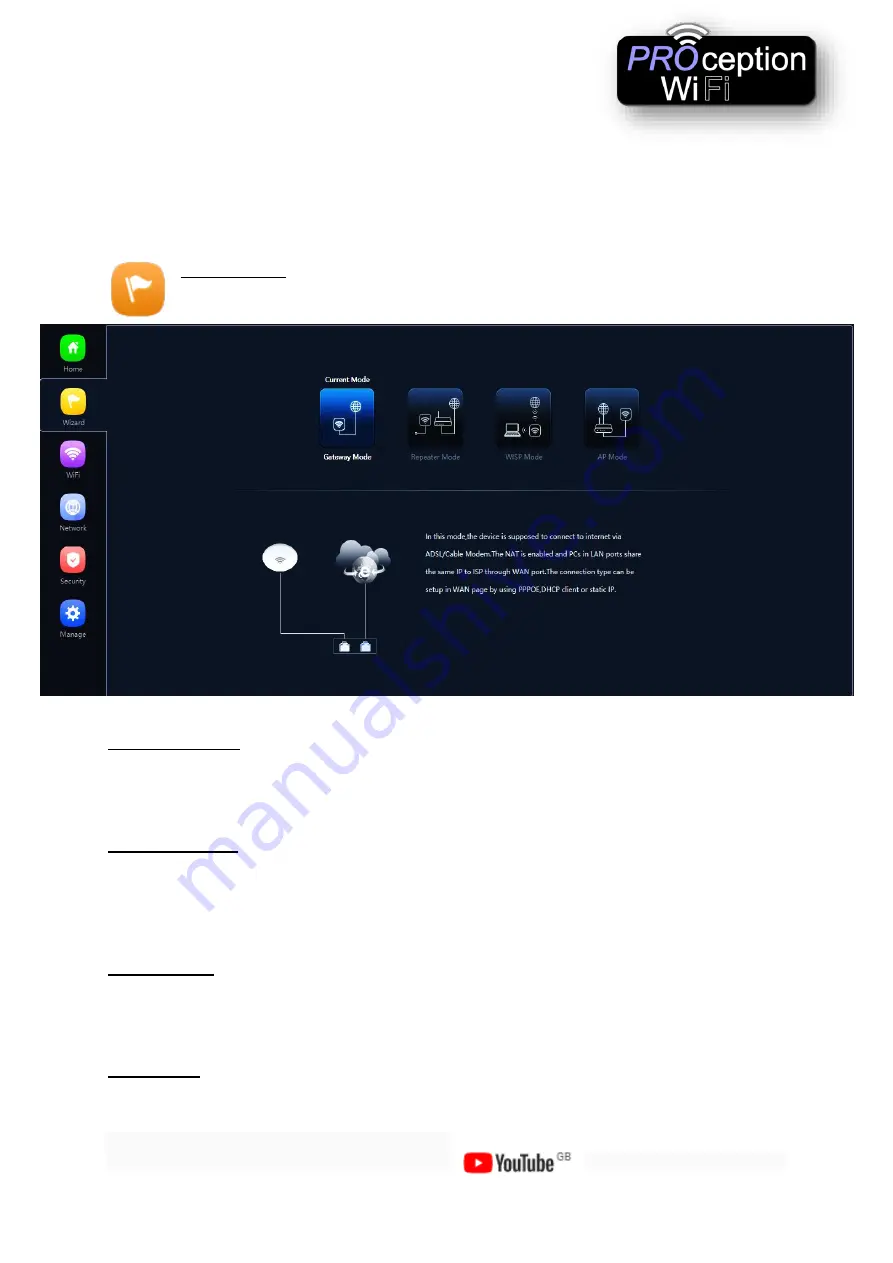
Setup Wizard
The mode the access point will work in
Gateway mode: -
The AP will allocate IP numbers to the connected devices. This mode is
default as it permits you to connect and setup the AP very easily.
The AP could be left in this mode however, any connections to the AP (Wireless or not) will
be allocated different IP addresses to the main network, potentially preventing
communication between devices on the main network.
Repeater mode:-
The AP will receive & retransmit the Wi-Fi signal from another device.
It performs the same role as Access Point mode, but the key is that it talks over Wi-Fi
instead. As such, this doesn’t get around obstacles as well as an access point does. While
an access point can be put in front of an obstacle, a repeater will need to be angled around
it. However, the benefit of repeaters is that t
hey don’t need a cable to connect to the central
hub.
WISP mode: -
wirelessly connects to a WISP (Wireless Internet Service Provider) AP. In this
mode, the AP also acts as a router for wired clients on your LAN and provides NAT (Network
Address Translation) and a DHCP server to generate IP addresses for wired clients only.
NAT and the DHCP server allow many computers to share the same wireless Internet
connection.
AP mode: -
Using Access Point mode is ideal if you want to extend the WiFi range, but the






























