24
PM-1440BV v3 2020-10
Copyright © 2020 Quality Machine Tools, LLC
Figure B
Quick alignment check
Figure A
Center-to-center axis
When headstock alignment really matters
Headstock alignment may not matter for center turning, but
it's critical when the workpiece is held in a chuck or a collet
— often about 90% of the workload in a typical model shop.
Assuming no appreciable deflection of the workpiece (too thin,
too far from the chuck), taper problems in a chuck/collet setup
are due to misalignment of the spindle axis relative to the lathe
bed. This is usually correctable by re-aligning the headstock.
Misalignment of the spindle by even the smallest fraction of
a degree causes a very measurable taper, even over short
lengths of material. For example, a misalignment as small as
one hundredth of a degree
will give a taper of 0.001” in 3
inches. If the headstock is (say) 10 inches long, this would be
corrected by tapping one end of the headstock forward or back
ALIGNING THE LATHE
The most important attribute of a properly set up lathe is its
ability to “machine parallel”, to cut a cylinder of uniform diame-
ter over its entire length. In other words, no taper.
Leveling of the lathe is a part of this, see Section 1. Equally
important is the alignment of the center-to-center axis with the
lathe bed, as seen
from above
. [Vertical alignment is nowhere
near as critical, rarely a cause of taper unless the lathe is dam-
aged or badly worn.]
How to align lathe centers
Practically all lathes come with some means of offsetting the
tailstock, typically for taper turning. For routine operations, the
offset must be zero, Figure A.
Precise method
This method uses a precision ground steel rod at least 10"
long. Look for 3/4 or 1 inch "drill rod" with a diameter tolerance
of ± 0.001" or less.
Straightness and uniform diameter are both important
(absolute diameter is not).
1. Set the rod in a collet chuck, or independent 4-jaw chuck,
with the outer end about 1/2 inch clear of the chuck.
2. Use a dial indicator to check for runout. If using a 4-jaw
adjust as necessary for minimum TIR (aim for 0.0005" or
less).
3. Center-drill the end of the ground rod.
4. Reverse the rod, re-adjust for minimum TIR, then drill the
other end.
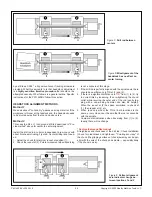
5. Set the drill rod snugly between centers, as Figure C. Lock
the tailstock.
6.
Set a dial indicator on the cross slide (to eliminate vertical
error use a flat disc contact, not the usual spherical type —
if a disc contact is not available, machine a cap to fit over
the spherical point).
7.
Starting at location (1), note which way the pointer rotates
when the cross slide is moved inward. In this setup the
pointer is assumed to turn clockwise as the cross slide
moves in.
8. Pre-load the indicator by a few thousandths, then traverse
the saddle from end to end. In a perfect the setup the point-
er will not move at all.
If the pointer turns clockwise as you go toward the tailstock,
as Figure C, the tailstock is biased to the front. This will cause
the lathe to cut a tapered workpiece with the larger diameter
at the headstock end. Correct this by a series of
very small
adjustments to the tailstock offset.
Another important question has to do with headstock/spindle
alignment relative to the lathe bed. For turning
between cen-
ters
this doesn't matter at all; the headstock can be wildly out
of square, Figure D, but the lathe will still machine parallel if
the centers have been aligned as previously described.
The scale usually provided on the tailstock is not reliable
for precision work
— think of it as only a starting point. What
follows are two methods for aligning centers, one quick and
easy, the other more precise.
Quick method
This method works only if the centers are in new condition,
sharp and clean.
1.
Carefully clean the taper sockets and the tapers them-
selves. Install the tapers.
2.
Move the saddle left as far as it will go, then slide the
tailstock left to touch the saddle.
3.
Lock the tailstock (this is important — unlocked to locked
can mean an offset of several thousandths).
4.
Advance the tailstock quill to bring the centers together.
5.
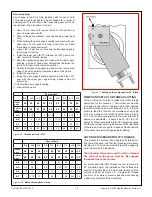
Place a scrap of hard shim stock or an old-style dou-
ble-edge razor blade between the centers, Figure B.
6.
Advance the tailstock quill to trap the blade, then lock the
quill. If the centers are aligned, the blade will point squarely
front to back. If not, adjust the tailstock offset by a series of
very small adjustments.
7.
If the range of quill motion permits, check the blade align-
ment at various extensions of the quill. There should be no
appreciable variation.