- 17 -
in that they specify a stand-alone authentication protocol be used
within an encrypted tunnel. TTLS supports any protocol within its
tunnel, including CHAP, MS-CHAP, MS-CHAPv2, PAP and
EAP-MD5. PEAP specifies that an EAP-compliant authentication
protocol must be used; this card supports EAP-MSCHAP v2,
EAP-TLS/Smart card and Generic Token Card. The client
certificate is optional required for the authentication.
TLS/Smart Card
–TLS is the most secure of the EAP protocols
but not easy to use. It requires that digital certificates be
exchanged in the authentication phase. The server presents a
certificate to the client. After validating the server’s certificate, the
client presents a client certificate to the server for validation.
MD5-Challenge –
MD5-Challenge is the easiest EAP Type. It
requires the wireless station to enter a set of user name and
password as the identity to RADIUS Server.
Session Resumption
There are “Disabled”, “Reauthentication”, “Roaming”, “SameSsid”
and “Always” selections for you to choose whether to recovery the
session in different status.
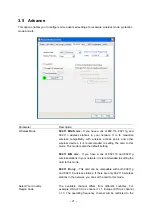
Identity
Enter the name as the identity for the server.
Password
Enter the password as the identity for the server.
Use Client Certificate
A client certificate is required for TLS, and is optional for TTLS and
PEAP. This forces a client certificate to be selected from the
appropriate Windows Certificate Store and made available to the
RADIUS server for certification.
Tunneled Authentication
Protocol
When the authentication type is PEAP or TTLS, select a protocol
to be used to build the encrypted tunnel.
Identity
This is the protected user EAP Identity used for authentication.
The identity specified may contain up to 63 ASCII characters, is
case sensitive and takes the form of a Network Access Identifier,
consisting of <name of the user>@<user’s home realm>. The
user’s home realm is optional and indicates the routing domain.
Password
The password used for authentication. It may contain up to 63
ASCII characters and is case sensitive.