17
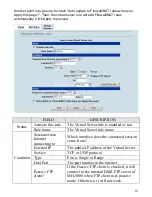
Virtual Server Settings
Virtual Servers
are computers connected using the
DMZ
port. They act as servers
to provide services to your LAN ports or other Internet users on the WAN ports. The
Virtual Server setting page maps one global IP address
-
an IP address that is valid
on the Internet, usually assigned by your ISP
-
to one local IP address from the IP
address range assigned to the MH-5000
’
s
DMZ
port. The default DMZ IP address is
10.1.1.254, so the servers
’
IP must range from 10.1.1.1 to 10.1.1.253, with a subnet
mask of 255.255.255.0.
Figure 2 Internet host connects to the Virtual Server behind MH-5000.
As the above Figure 2 illustrated, the server 10.1.1.5 provides FTP service and is
located on the DMZ region behind MH-5000. By this way, MH-5000 will act as a
Virtual Server role which redirects the packets to the real server 10.1.1.5. And you
can announce to the internet users that the ftp server ip/port is 61.2.1.1/44444. So,
all of the internet users can connect the 61.2.1.1/44444 to get ftp service.
An example virtual server:
Customize the rule name as the ftpServer. For any
packets with its destination IP equaling to the WAN1 IP (61.2.1.1) and destination
port equaling to 44444, ask MH-5000 to translate the packet
’
s destination IP/port
into 10.1.1.5/21. Check the
Passive FTP client
at this port to maximize the
compatibility of the FTP protocol. This is useful if you want to provide connectivity to
passive FTP clients. For passive FTP clients, the server will return them the private
IP address and the port number for them to connect back to do data transmissions.
Since the private IP from them cannot be routed to our zone, the data connections
would fail. After enabling this feature, the MH-5000 will translate the private IP/port
into an IP/port of its own. Thus the problem is gracefully solved.