48
SEBU8337
Maintenance Section
Re
fi
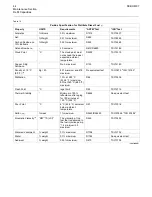
ll Capacities
Raw pressed vegetable oils are NOT acceptable for
use as a fuel in any concentration in compression
engines. Without esteri
fi
cation, these oils gel in the
crankcase and the fuel tank. These fuels may not be
compatible with many of the elastomers that are used
in engines that are manufactured today. In original
forms, these oils are not suitable for use as a fuel
in compression engines. Alternate base stocks for
biodiesel may include animal tallow, waste cooking
oils, or a variety of other feedstocks. In order to use
any of the products that are listed as fuel, the oil
must be esteri
fi
ed.
Note:
Engines that are manufactured by Perkins
are certi
fi
ed by use of the prescribed Environmental
Protection Agency (EPA) and European Certi
fi
cation
fuels. Perkins does not certify engines on any other
fuel. The user of the engine has the responsibility
of using the correct fuel that is recommended by
the manufacturer and allowed by the EPA and other
appropriate regulatory agencies.
Recommendation for the use of biodiesel
The neat biodiesel must conform to “EN14214” or
“ASTM D6751” regulations. A maximum of 30%
mixture of biodiesel can be used in mineral diesel fuel.
The mineral diesel fuel must conform to “EN590”,
“ASTM D975” or “BS2869 Grade A2” regulations.
Note:
When biodiesel, or any blend of biodiesel is
used, the user has the responsibility for obtaining the
proper local exemptions, regional exemptions, and/or
national exemptions that are required for the use
of biodiesel in any Perkins engine that is regulated
by emissions standards. Biodiesel that meets EN
14214 is acceptable. The biodiesel must be blended
with an acceptable distillate diesel fuel at the
maximum stated percentages. However, the following
operational recommendations must be followed:
•
The oil change interval can be affected by the use
of biodiesel. Use Services Oil Analysis in order
to monitor the condition of the engine oil. Use
Services Oil Analysis also in order to determine the
oil change interval that is optimum.
•
Con
fi
rm that biodiesel is acceptable for use with
the manufacturer of the fuel
fi
lters.
•
In a comparison of distillate fuels to biodiesel,
biodiesel provides less energy per gallon by 5% to
7%. Do NOT change the engine rating in order to
compensate for the power loss. This will help avoid
engine problems when the engine is converted
back to 100 percent distillate diesel fuel.
•
The compatibility of the elastomers with biodiesel
is being monitored. The condition of seals and
hoses should be monitored regularly.
•
Biodiesel may pose low ambient temperature
problems for both storage and operation. At low
ambient temperatures, fuel may need to be stored
in a heated building or a heated storage tank. The
fuel system may require heated fuel lines,
fi
lters,
and tanks. Filters may plug and fuel in the tank may
solidify at low ambient temperatures if precautions
are not taken. Consult your biodiesel supplier for
assistance in the blending and attainment of the
proper cloud point for the fuel.
•
Biodiesel has poor oxidation stability, which
can result in long term problems in the storage
of biodiesel. The poor oxidation stability may
accelerate fuel oxidation in the fuel system.
This is especially true in engines with electronic
fuel systems because these engines operate at
higher temperatures. Consult the fuel supplier for
oxidation stability additives.
•
Biodiesel is a fuel that can be made from a variety
of feedstock. The feedstock that is used can
affect the performance of the product. Two of the
characteristics of the fuel that are affected are
cold
fl
ow and oxidation stability. Contact your fuel
supplier for guidance.
•
Biodiesel or biodiesel blends are not recommended
for engines that will operate occasionally. This
is due to poor oxidation stability. If the user is
prepared to accept some risk, then limit biodiesel
to a maximum of B5. Examples of applications that
should limit the use of biodiesel are the following:
Standby Generator sets and certain emergency
vehicles
•
Biodiesel is an excellent medium for microbial
contamination and growth. Microbial contamination
and growth can cause corrosion in the fuel system
and premature plugging of the fuel
fi
lter. The
use of conventionalanti-microbial additives and
the effectiveness of conventional anti-microbial
additives in biodiesel is not known. Consult your
supplier of fuel and additive for assistance.
•
Care must be taken in order to remove water
from fuel tanks. Water accelerates microbial
contamination and growth. When biodiesel is
compared to distillate fuels, water is naturally more
likely to exist in the biodiesel.
Fuel for Cold Weather Operation
The European standard “EN590” contains climate
dependant requirements and a range of options. The
options can be applied differently in each country.
There are 5 classes that are given to arctic climates
and severe winter climates. 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4.