13
to incorrect readings and costly errors. Therefore, in an effort to prevent the common mistakes associated with
customer-performed calibration, this document includes a broad overview of the Back-to-Back Calibration
technique. This technique provides a quick and easy method for determining the sensitivity of a test
accelerometer over a wide frequency range.
6.1.2 BACK-TO-BACK CALIBRATION THEORY
Back-to-Back Calibration is perhaps the most common method for determining the sensitivity of piezoelectric
accelerometers. This method relies on a simple comparison to a previously calibrated accelerometer, typically
referred to as a reference standard.
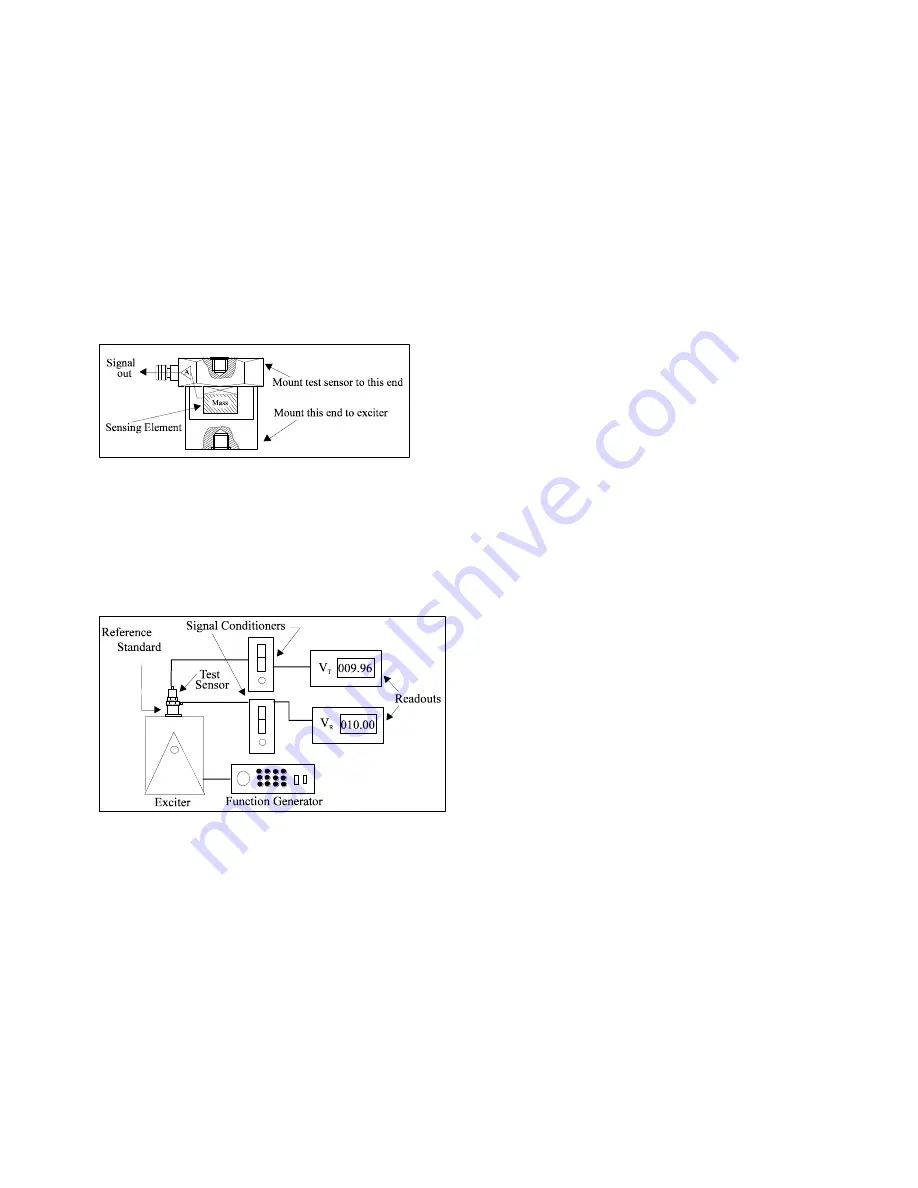
Figure 1.
Reference Standard Accelerometer
These high-accuracy devices, which are directly traceable to a recognized standards laboratory, are designed
for stability, as well as configured to accept a test accelerometer. By mounting a test accelerometer to the
reference standard and then connecting this combination to a suitable vibration source, it is possible to vibrate
both devices and compare the data as shown in Figure 2. (Test set-ups may be automated and vary,
depending on the type and number of accelerometers being calibrated.)
Figure 2.
Typical Back-to-Back Calibration System
Because the acceleration is the same on both sensors, the ratio of their outputs (V
T
/V
R
) must also be the ratio
of their sensitivities. With the sensitivity of the reference standard (S
R
) known, the exact sensitivity of the test
sensor (S
T
) is easily calculated by using the following equation:
S
T
= S
R
(V
T
/V
R
)
By varying the frequency of the vibration, the sensor may be calibrated over its entire operating frequency
range. The typical response of an unfiltered accelerometer is shown in Figure 3.
Summary of Contents for EX619A11
Page 23: ...DWG 62689 REV NR DIN 44641...
Page 24: ...DWG 62689 REV NR DIN 44641...
Page 25: ...DWG 62689 REV NR DIN 44641...
Page 26: ...DWG 62690 REV NR DIN 44641...
Page 27: ...DWG 62690 REV NR DIN 44641...
Page 28: ...DWG 62690 REV NR DIN 44641...
















































