7
For assistance, call toll-free at 800-343-4048
Startup
Oxygen
Analyzer
Calibration
Operation/Calibration (Model HFX0-3)
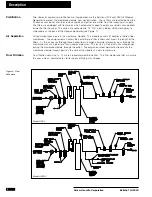
Plug the IEC power cord into the power entry receptacle of the generator, and plug the opposite end
into a nearby wall outlet with earth ground protection. (Note:
Note:
Note:
Note:
Note: There is no power switch on the genera-
tor. The oxygen analyzer is energized when the generator is plugged in.)
The inlet and outlet connections to the Balston HFX0-3 Nitrogen Generator must be checked for leaks
prior to system start-up. After the system is properly installed and checked for leaks, the inlet gate
valve can be opened to introduce compressed air to the system.
During start-up and adjustment of the system, the nitrogen produced by the system will vary in purity.
If the application for the nitrogen is critically dependent on purity, the nitrogen produced during start-up
or adjustment should be vented.
If the outlet nitrogen flow is closed, the system will still consume compressed air. The inlet air is simply
vented to atmosphere through the permeate ports of the membrane module.
CAUTION: the oxygen analyzer will not provide accurate readings unless calibrated on a regular
CAUTION: the oxygen analyzer will not provide accurate readings unless calibrated on a regular
CAUTION: the oxygen analyzer will not provide accurate readings unless calibrated on a regular
CAUTION: the oxygen analyzer will not provide accurate readings unless calibrated on a regular
CAUTION: the oxygen analyzer will not provide accurate readings unless calibrated on a regular
basis.
basis.
basis.
basis.
basis.
The oxygen analyzer is calibrated prior to shipment; however, Parker strongly recommends re-
calibrating the unit prior to initial start-up. After the initial start-up, the analyzer should be calibrated on
a bi-weekly basis until a suitable schedule is determined, based upon the level of accuracy required by
the application.
There are two methods of calibrating the oxygen analyzer: the two point method and the single point
method. In the two point method, the first point in the calibration range is set to zero using a zero gas
(zero percent oxygen), and the second point in the range is set to a known percentage of oxygen using
a span gas (known quantity of oxygen, per gas supplier) or compressed air (20.9% oxygen). In the
single point method, only one point in the calibration range is set, using either span gas or compressed
air. Maximum accuracy in oxygen concentration monitoring will be achieved if the oxygen concentra-
tion in the span gas is within the range of the expected oxygen concentration in the process stream
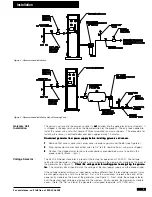
and the pressure of the gas closely approximates the pressure of the nitrogen gas (See Figure 3 for
calibration controls).
The procedure for the two point calibration method
two point calibration method
two point calibration method
two point calibration method
two point calibration method is as follows:
1
1
1
1
1 Throw the toggle switch on the back of the unit to the upright position, toward the calibration port.
2
2
2
2
2 Connect a tank of zero gas to the port. (Gas pressure should be approximately equal to operating
pressure.)
3
3
3
3
3 Allow the zero gas to flow through the unit until the reading on the oxygen concentration display
stabilizes.
4
4
4
4
4 Adjust the zero potentiometer until the oxygen concentration display reads zero.
5
5
5
5
5 Disconnect the zero gas from the calibration port, and connect a tank of span gas (operating
pressure) or a source of clean compressed air.
6
6
6
6
6 Allow the reading to stabilize, and adjust the span potentiometer until the reading on the oxygen
concentration display reads the known percent (span gas) or 20.9% (compressed air).
7
7
7
7
7 Disconnect the calibration gas and throw the toggle switch to the downward position to resume
sampling the nitrogen stream.
The procedure for the single point calibration
single point calibration
single point calibration
single point calibration
single point calibration method
method
method
method
method is as follows:
1
1
1
1
1 Connect a tank of span gas (operating pressure) or a source of clean compressed air to the calibra-
tion port.
2
2
2
2
2 Allow the gas or air to flow through the analyzer until the reading on the oxygen concentration
display stabilizes.
3
3
3
3
3 Adjust span potentiometer until the reading on the oxygen concentration display reads the known
percent (span gas) or 20.9% (compressed air).
4
4
4
4
4 Disconnect the calibration gas and throw the toggle switch to the downward position to resume
sampling the nitrogen stream.
(Note: Parker recommends the use of a span gas with an oxygen content between 1% and 10%.)
!