12
The setting circles must be re-calibrated every time you wish
to locate a new object. Do so by calibrating the setting circles
for the centered object before moving on to the next one.
confused about Pointing the telescope?
Beginners occasionally experience some confusion about
how to point the telescope overhead or in other directions. In
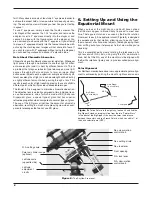
Figure 1 the telescope is pointed north as it would be during
polar alignment. The counterweight shaft is oriented down-
ward. But it will not look like that when the telescope is pointed
in other directions. Let’s say you want to view an object that is
directly overhead, at the zenith. How do you do it?
DO NOT make any adjustment to the latitude adjustment L-
bolts. That will spoil the mount’s polar alignment. Remember,
once the mount is polar aligned, the telescope should be
moved only on the R.A. and Dec. axes. To point the scope
overhead, first loosen the R.A. lock lever and rotate the tele-
scope on the right ascension axis until the counterweight
shaft is horizontal (parallel to the ground). Then loosen the
Dec. lock lever and rotate the telescope until it is pointing
straight overhead. The counterweight shaft is still horizontal.
Then retighten both lock levers.
What if you need to aim the telescope directly north, but at an
object that is nearer to the horizon than Polaris? You can’t do
it with the counterweight down as pictured in Figure 1. Again,
you have to rotate the scope in right ascension so that the
counterweight shaft is positioned horizontally. Then rotate the
scope in declination so it points to where you want it near the
horizon.
To point the telescope directly south, the counterweight shaft
should again be horizontal. Then you simply rotate the scope
on the declination axis until it points in the south direction.
To point the telescope to the east or west, or in other direc-
tions, you rotate the telescope on its right ascension and
declination axes. Depending on the altitude of the object you
want to observe, the counterweight shaft will be oriented
somewhere between vertical and horizontal.
Figure 14 illustrates how the telescope will look when pointed
at the four cardinal directions: north, south, east and west.
7. astronomical observing
For many users, the SkyView Pro 80mm ED EQ telescope
will be a major leap into the world of amateur astronomy. This
section is intended to get you ready for your voyages through
the night sky.
site selection
Pick a location away from street lights and bright yard light-
ing. Avoid viewing over rooftops and chimneys, as they often
have warm air currents rising from them which distort the
image seen in the eyepiece. Similarly, you should not observe
through an open or closed window from indoors. Better yet,
choose a site out-of-town, away from any “light pollution”.
You’ll be stunned at how many more stars you’ll see! Most
importantly, make sure that any chosen site has a clear view
of a large portion of the sky.
seeing and transparency
Atmospheric conditions play a huge part in quality of view-
ing. In conditions of good “seeing”, star twinkling is minimal
and objects appear steady in the eyepiece. Seeing is best
overhead, worst at the horizon. Also, seeing generally gets
better after midnight, when much of the heat absorbed by the
Earth during the day has radiated off into space. Typically,
seeing conditions will be better at sites that have an altitude
over about 3000 feet. Altitude helps because it decreases
the amount of distortion causing atmosphere you are looking
through.
A good way to judge if the seeing is good or not is to look at
bright stars about 40° above the horizon. If the stars appear to
“twinkle”, the atmosphere is significantly distorting the incom-
ing light, and views at high magnifications will not appear
sharp. If the stars appear steady and do not twinkle, seeing
conditions are probably good and higher magnifications will
be possible. Also, seeing conditions are typically poor during
the day. This is because the heat from the Sun warms the air
and causes turbulence.
Good “transparency” is especially important for observ-
ing faint objects. It simply means the air is free of moisture,
smoke, and dust. All tend to scatter light, which reduces an
object’s brightness.
One good way to tell if conditions are good is by how many
stars you can see with your naked eye. If you cannot see
stars of magnitude 3.5 or dimmer, then conditions are poor.
Magnitude is a measure of how bright a star is; the brighter a
star is, the lower its magnitude will be. A good star to remem-
Figure 14a‑d.
This illustration shows the telescope pointed in
the four cardinal directions (a) north, (b) south, (c) east, (d) west.
Note that the tripod and mount have been moved; only the telescope
tube has been moved on the R.A. and Dec. axes.
a
b
c
d