9
In conditions of good seeing, star twinkling is minimal and
images appear steady in the eyepiece. Seeing is best over-
head, worst at the horizon. Also, seeing generally gets better
after midnight, when much of the heat absorbed by the Earth
during the day has radiated off into space.
Especially important for observing faint objects is good “trans-
parency”—air free of moisture, smoke, and dust. All tend to
scatter light, which reduces an object’s brightness.
Transparency is judged by the magnitude of the faintest stars
you can see with the unaided eye (6th magnitude or fainter is
desirable).
One good way to tell if conditions are good is by how many
stars you can see with your naked eye. If you cannot see stars
of magnitude 3.5 or dimmer then conditions are poor.
Magnitude is a measure of how bright a star is, the brighter a
star is, the lower its magnitude will be. A good star to remem-
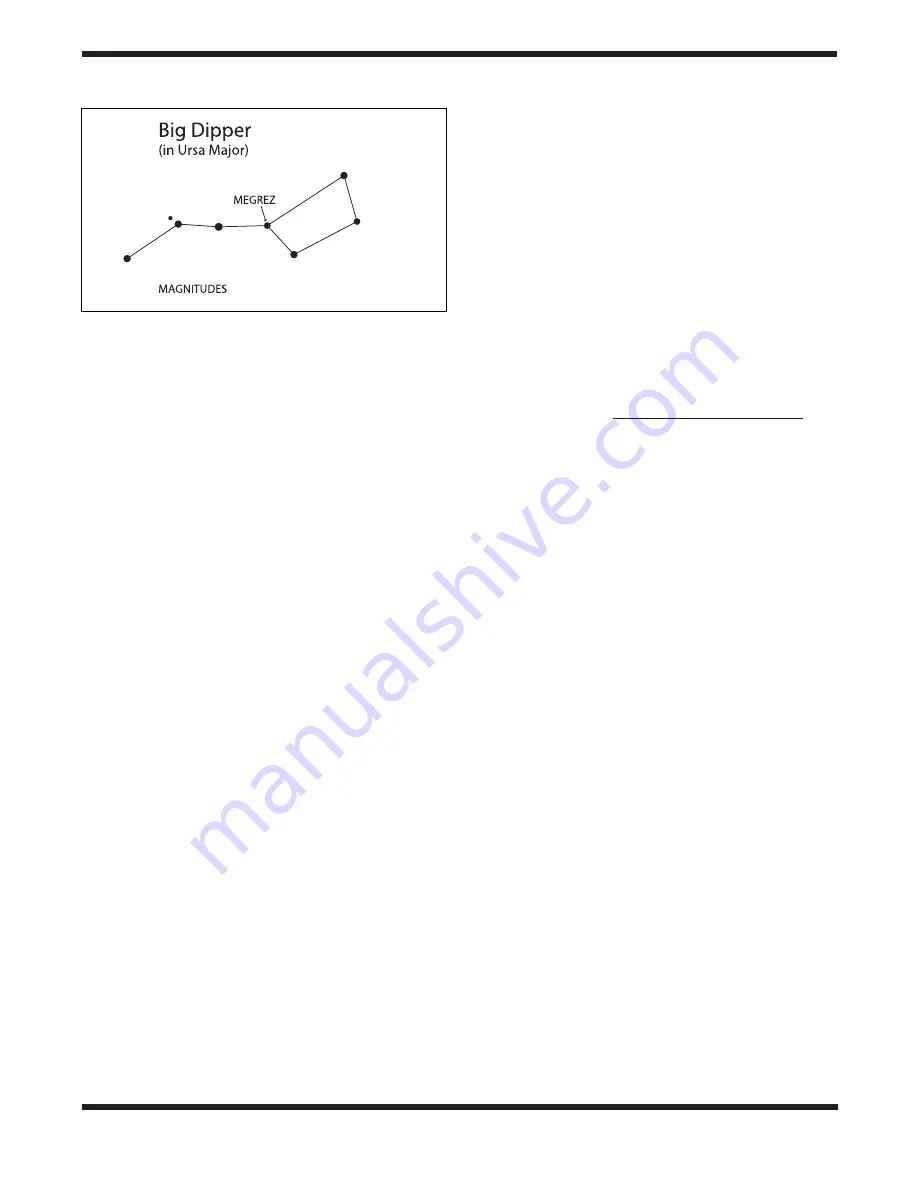
ber for this is Megrez (mag. 3.4), which is the star in the “Big
Dipper” connecting the handle to the “dipper”. If you cannot
see Megrez, then you have fog, haze, clouds, smog, or other
conditions that are hindering your viewing. (See Figure 7)
Cooling the Telescope
All optical instruments need time to reach “thermal equilibri-
um.” The bigger the instrument and the larger the temperature
change, the more time is needed. Allow at least 30 minutes for
your telescope to cool to the temperature outdoors.
Let Your Eyes Dark-Adapt
Don’t expect to go from a lighted house into the darkness of
the outdoors at night and immediately see faint nebulas,
galaxies, and star clusters—or even very many stars, for that
matter. Your eyes take about 30 minutes to reach perhaps
80% of their full dark-adapted sensitivity. As your eyes
become dark-adapted, more stars will glimmer into view and
you’ll be able to see fainter details in objects you view in your
telescope.
To see what you’re doing in the darkness, use a red-filtered
flashlight rather than a white light. Red light does not spoil
your eyes’ dark adaptation like white light does. A flashlight
with a red LED light is ideal, or you can cover the front of a
regular incandescent flashlight with red cellophane or paper.
Beware, too, that nearby porch and streetlights and car head-
lights will ruin your night vision.
Eyepiece Selection
By using eyepieces of varying focal lengths, it is possible to
attain many magnifications with the SpaceProbe 3 EQ. The
SpaceProbe 3 EQ comes with two Explorer II eyepieces, a
25mm and a 10mm. These give magnifications of 28x and 70x
respectively. Other eyepieces can be used to achieve higher
or lower powers. It is quite common for an observer to own five
or more eyepieces to access a wide range of magnifications.
This allows the observer to choose the best eyepiece to use
depending on the object being viewed.
To calculate the magnification, or power, of a telescope and
eyepiece combination, simply divide the focal length of the tel-
escope by the focal length of the eyepiece:
Telescope Focal Length (mm)
Magnification =
Eyepiece Focal Length (mm)
For example, the SpaceProbe 3 EQ, which has a focal length
of 700mm, used in combination with the 25mm eyepiece,
yields a power of:
700mm ÷ 25mm = 28x
Every telescope has a useful limit of power of about 2x per
mm of aperture (about 152x for the SpaceProbe 3 EQ).
Claims of higher power by some telescope manufacturers are
a misleading advertising gimmick and should be dismissed.
Keep in mind that at higher powers, an image will always be
dimmer and less sharp (this is a fundamental law of optics).
The steadiness of the air (the “seeing”) will also limit how
much magnification an image can tolerate.
Whatever you choose to view, always start by inserting your
lowest-power (longest focal length) eyepiece to locate and
center the object. Low magnification yields a wide field of
view, which shows a larger area of sky in the eyepiece. This
makes acquiring and centering an object much easier. If you
try to find and center objects with high power (narrow field of
view), it’s like trying to find a needle in a haystack!
Once you’ve centered the object in the eyepiece, you can
switch to higher magnification (shorter focal length eyepiece),
if you wish. This is especially recommended for small and
bright objects, like planets and double stars. The Moon also
takes higher magnifications well.
The best rule of thumb with eyepiece selection is to start with
a low power, wide-field eyepiece, and then work your way up
in magnification. If the object looks better, try an even higher
magnification. If the object looks worse, then back off the
magnification a little by using a lower-power eyepiece.
What to Expect
So what will you see with your telescope? You should be able
to see bands on Jupiter, the rings of Saturn, craters on the
Moon, the waxing and waning of Venus, and many bright
deep-sky objects. Do not expect to see any color as you do in
NASA photos, since those are taken with long-exposure cam-
Figure 7.
Megrez connects the Big Dipper’s handle to it’s
“pan”. It is a good guide to how conditions are. If you can not
see Megrez (a 3.4 mag star) then conditions are poor.
2.4
1.7
3.4
2.4
4.9
1.9
1.9
2.5
Summary of Contents for SpaceProbe 3 EQ 9844
Page 15: ...15 ...