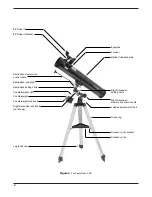
telescope should now be able to rotate freely about the
R.A. axis. Rotate it until the counterweight shaft is parallel
to the ground (i.e., horizontal)
2. Now loosen the counterweight lock knob and slide the
weight along the shaft until it exactly counterbalances the
telescope (Figure 3a). That’s the point at which the shaft
remains horizontal even when you let go of the telescope
with both hands (Figure 3b).
3. Retighten the counterweight lock knob. The telescope is
now balanced in the right ascension axis. The telescope is
already balanced in the declination axis.
Now when you loosen the lock knob on one or both axes and
manually point the telescope, it should move without resist-
ance and should not drift from where you point it.
Focusing the Telescope
Insert the 25mm Explorer II eyepiece into the focuser and
secure with the thumbscrew. Move the telescope so the front
(open) end is pointing in the general direction of an object at
least 1/4-mile away. Now with your fingers, slowly rotate one
of the focusing knobs until the object comes into sharp focus.
Go a little bit beyond sharp focus until the image starts to blur
again, then reverse the rotation of the knob, just to make sure
you’ve hit the exact focus point.
Do You Wear Eyeglasses?
If you wear eyeglasses, you may be able to keep them on
while you observe. In order to do this, your eyepiece must
have enough “eye relief” to allow you to see the entire field of
view with glasses on. You can try this by looking through the
eyepiece first with your glasses on and then with them off, and
see if the glasses restrict the view to only a portion of the full
field. If the glasses do restrict the field of view, you may be
able to observe with your glasses off by just refocusing the
telescope the needed amount.
If your eyes are astigmatic, images will probably appear the
best with glasses on. This is because a telescope’s focuser can
accommodate for nearsightedness or farsightedness, but not
astigmatism. If you have to wear your glasses while observing
and cannot see the entire field of view, you may want to pur-
chase additional eyepieces that have longer eye relief.
Operating the EZ Finder II reflex finder
The EZ Finder II reflex finder (Figure 4) works by projecting a
tiny red dot onto a lens mounted in the front of the unit. When
you look through the EZ Finder II, the red dot will appear to float
in space, helping you locate even the faintest of deep space
objects. The red dot is produced by a light-emitting diode (LED),
not a laser beam, near the rear of the sight. A replaceable 3-volt
lithium battery provides the power for the diode.
To use the EZ Finder II, turn the power knob clockwise until
you hear a “click” indicating that power has been turned on.
Figure 3.
Proper operation of the equatorial mount requires
balancing the telescope tube on the R.A. axis (a). With the R.A. lock
knob released, slide the counterweight along the counterweight
shaft until it just counterbalances the tube (b). When you let go with
both hands, the tube should not drift up or down.
5
®
Figure 4.
The EZ Finder II.
a.
b.
Azimuth knob
Power knob
Altitude
knob
Metal
thumbnuts
Battery
casing
Summary of Contents for SpaceProbe 3 EQ 9844
Page 15: ...15 ...