8
To find Polaris in the sky, look north and locate the pattern of
the Big Dipper (Figure 7). The two stars at the end of the
“bowl” of the Big Dipper point right to Polaris.
Observers in the Southern Hemisphere aren’t so fortunate to
have a bright star so near the south celestial pole (SCP). The
star Sigma Octantis lies about 1° from the SCP, but it is bare-
ly visible with the naked eye (magnitude 5.5).
For general visual observation, an approximate polar align-
ment is sufficient.
1. Level the equatorial mount by adjusting the length of the
three tripod legs.
2. There are two latitude adjustment L-bolts (see Figure 6);
loosen one while tightening the other. By doing this you
will adjust the latitude of the mount. Continue adjusting the
mount until the pointer on the latitude scale is set at the
latitude of your observing site. If you don’t know your lati-
tude, consult a geographical atlas to find it. For example, if
your latitude is 35° North, set the pointer to 35. The lati-
tude setting should not have to be adjusted again unless
you move to a different viewing location some distance
away.
3. Loosen the Dec. lock lever and rotate the telescope’s opti-
cal tube until it is parallel with the right ascension axis, as
it is in Figure 6.
4. Move the tripod so the telescope tube and right ascension
axis point roughly at Polaris. If you cannot see Polaris
directly from your observing site, consult a compass and
rotate the tripod so the telescope points north. There is a
label bearing a large “N” at the base of the equatorial
mount (Figure 8); it should be facing north.
The equatorial mount is now polar aligned for casual observing.
More precise polar alignment is recommended for astro-
photography. For this we suggest using the optional polar axis
finder scope
From this point on in your observing session, you should not
make any further adjustments to the latitude of the mount, nor
should you move the tripod. Doing so will undo the polar
alignment. The telescope should be moved only about its R.A.
and Dec. axes.
Polar Alignment Using an Optional Polar Axis
Finder Scope
The SkyView Pro 6LT EQ mount can be equipped with an
optional polar axis finder scope (Figure 9a) which goes inside
the right ascension axis of the mount. When properly aligned
and used, it makes accurate polar alignment quick and easy
to do.
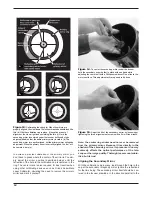
To install the polar axis finder scope, remove the cover at the
rear of the mount’s right ascension axis (Figure 9b) and
thread the polar axis finder scope into the equatorial mount
until tight.
Alignment of the Polar Axis Finder Scope
1. Look through the polar finder at a distant object (during
the day) and center it in the crosshairs. You may need to
adjust the latitude adjustment L-bolts and the tripod posi-
tion to do this.
2. Rotate the mount 180° about the R.A. axis. Again, it may
be convenient to remove the counterweights and optical
tube first.
3. Look through the polar finder again. Is the object being
viewed still centered on the crosshairs? If it is, then no fur-
Figure 8.
For polar alignment, position the tripod so that the “N”
label at the base of the mount faces north. The azimuth fine
adjustment knobs above it are used to make small adjustments to
the mount’s azimuth position. Be certain to loosen the tripod
attachment knob on the central support shaft before adjusting
these knobs.
Azimuth
adjustment
knobs
Figure 9a.
The optional polar axis finder scope.
Eyepiece
focus ring
Focus
lock ring
Objective
lens
Figure 9b.
Installing the optional polar axis finder scope.
Alignment
setscrews (3)
Summary of Contents for SKYVIEW PRO 6LT EQ 9872
Page 19: ...19 ...