26
Wiring
(continued)
Step Five
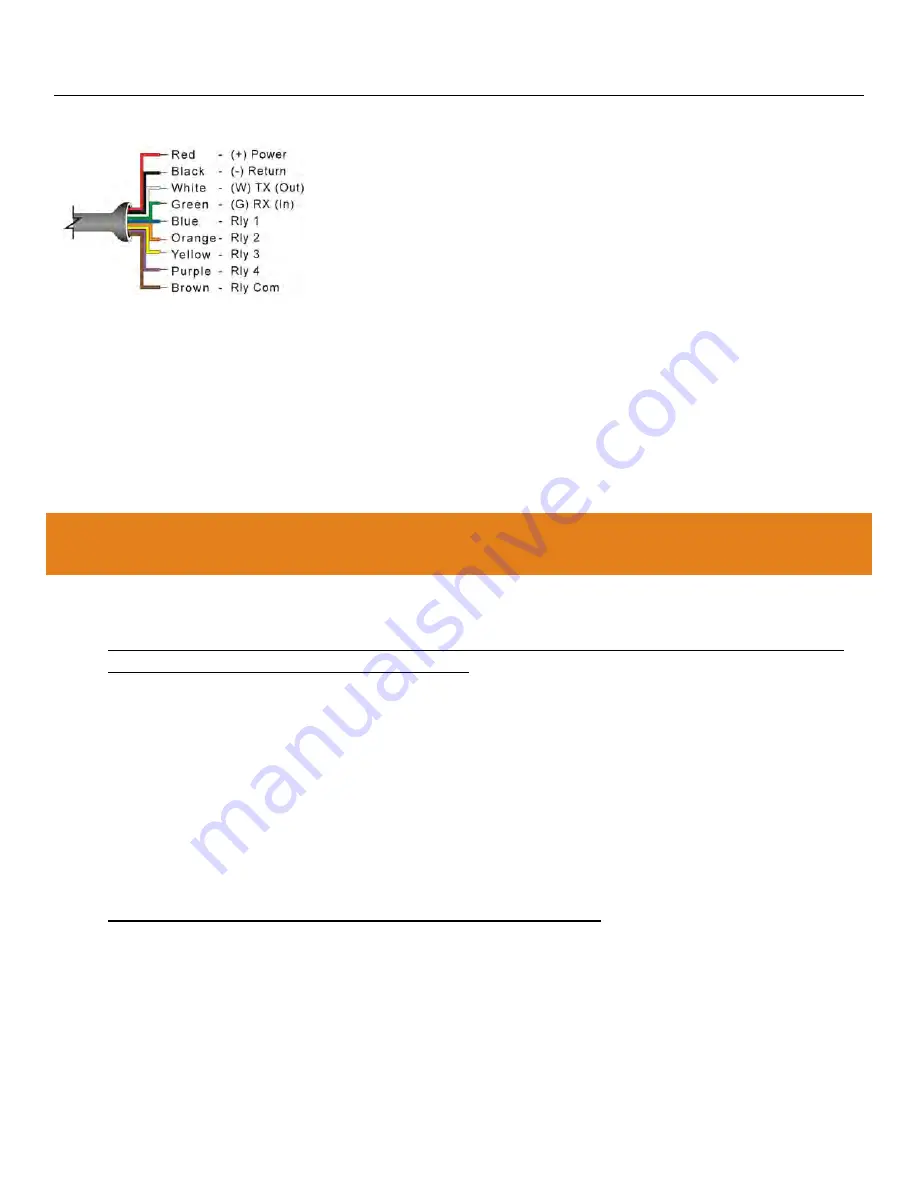
WIRE CONNECTIONS
Red (+) & Black (-):
Red [(+) Power] and Black [(-) Return] leads are for
connection to a 24 VDC power supply or to a 4-20 mA loop power
source. The red and black wires can be extended up to 1,000 feet using
a 22-gauge or larger wire.
White & Green:
White [(W) TX] and Green [(G) RX] leads are reserved
for use with LVCN414-SW. These wires should only be connected to
one device at a time (i.e. only to LVCN414-SW). In addition, these
wires should not be connected to LVCN414-SW while power is supplied
from any source other than the LVU500-USB series Fob. The maximum
cable distance between the computer and LVU500 series is 15’.
Note:
Never allow the white or green wires to touch any power supply.
LVU501 and LVU503 Series
Blue, Orange, Yellow, Purple & Brown:
Blue (RLY1), Orange (RLY2), Yellow (RLY3) & Purple (RLY4) wires are
the relay contacts (normally open) from each of the relays respectively. The Brown wire (RLY Common) is the
common for all the relays. Relay selection is determined by the configuration in LVCN414-SW. Relays are all dry
contacts so polarity can be revered from the example shown in the wiring diagram.
LVU500 series uses latching relays. When power is removed to the sensor, the relays will remain in their last state.
Ex: If the relay is energized, when power is removed, the relay will remain in an energized state.
GENERAL NOTES FOR ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS, USAGE AND SAFETY
Where personal safety or significant property damage can occur due to a spill, the installation
must have a redundant backup safety system.
Wiring should always be completed by a licensed electrician.
Supply voltage should never exceed 28 VDC.
Do not exceed 28 VDC power on the relays within LVU500 series.
Always use stepper relays between the sensor and external loads. For DC circuits use a catch diode
such as 1N4148, shown on the previous page.
Protect the sensor from excessive electrical spikes by isolating the power, whenever possible.
The sensor materials must be chemically compatible with the liquids to be measured.
Design a fail-safe system for possible sensor and/or power failure.
o
During power failure, relays will remain in their current state and will not change until power is
restored and the signal is reacquired.
Never use the sensor in environments classified as hazardous.
















































