10
Modbus Basics
10
Section 10 - Modbus Basics
Modbus is a “master-slave” system..., where the “master” communicates with one or multiple “slaves”.
The master typically is a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), DCS (Distributed Control System), HMI (Human Machine
Interface), RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) or PC.
The three most common Modbus versions used are: MODBUS ASCII, MODBUS RTU and MODBUS/TCP.
In Modbus RTU, data is coded in binary, and requires only one communication byte per data byte. This is ideal for use over
multi-drop RS485 networks, at speeds up to 115,200 bps.
The most common speeds are 9,600 bps and 19,200 bps.
Modbus RTU is the most widely used industrial protocol and is supported by the DRST-CM.
Modbus RTU:
To communicate with a slave device, the master sends a message containing:
Device Address - Function Code - Data - Error Check
The Device Address is a number from 0 to 247.
Messages sent to address 0 (broadcast messages) will be accepted by all slaves, but numbers 1-247 are addresses of specific
devices.
With the exception of broadcast messages, a slave device always responds to a Modbus message so the master knows the
message was received.
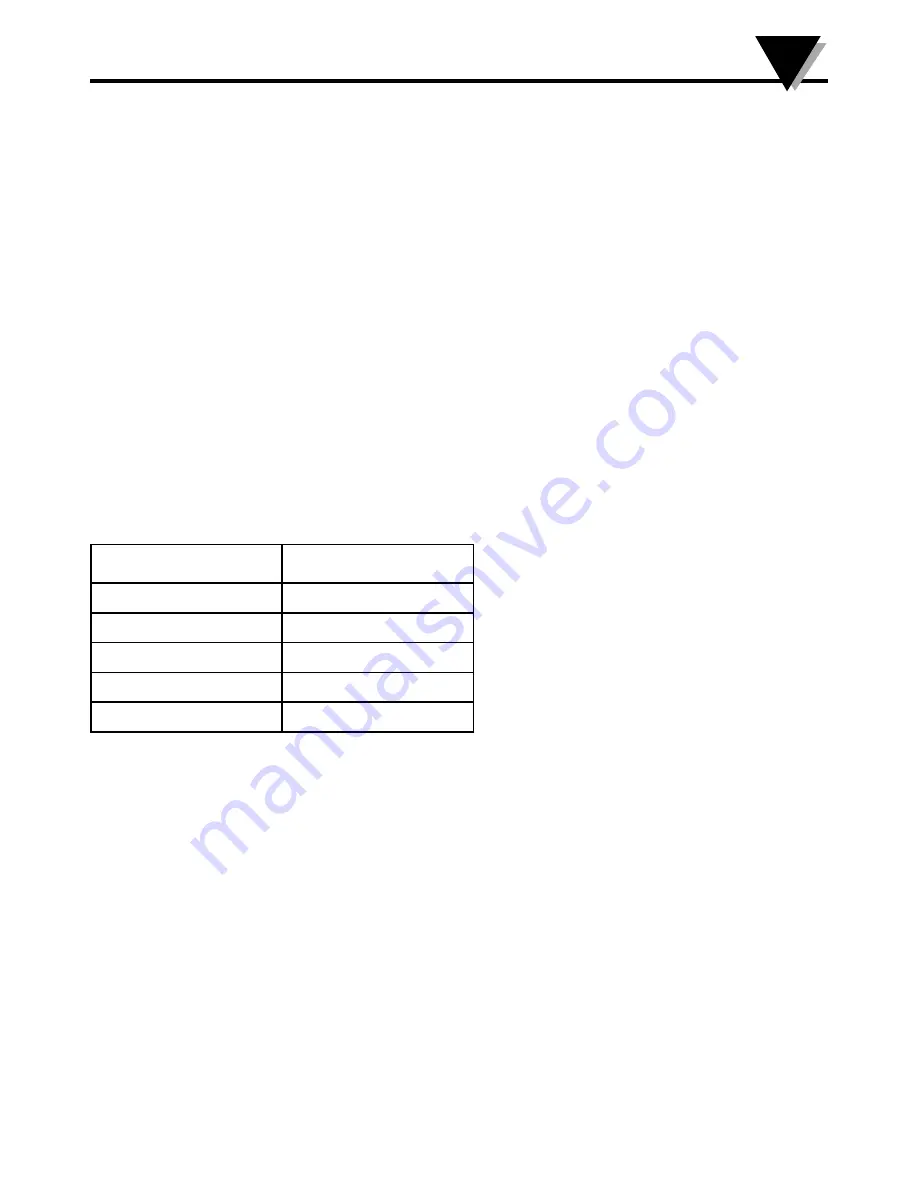
DRST-CM Supported Modbus Function Codes:
The Function Code defines the command that the slave device is to execute, such as read data, accept data, report status.
Some function codes have subfunction codes.
The Data defines addresses in the device’s memory map for read functions, contains data values to be written into the
device’s memory, or contains other information needed to carry out the function requested.
The Error Check is a 16-bit numeric value representing the Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC).
Maximum number of registers which can be read or written at once:
For a read command, the limit is 8 registers at a baud rate up to 38,400 bps, 16 registers @ 57,800 bps and 32 registers @
115,200 bps.
For a write command, the limit is 123 registers at baud rates up to 115,200 bps.
Command
Function code
Read Holding Registers
03
Read Input Registers
04
Write Single Register
06
Diagnostics
08
Write Multiple Registers
16

































