6
TECHNICAL FEATURES
GB
Table 1
Model
Code Speed
Power
Torque Consumption Weight Noise
Lp
Vibrations
a
h
Clutch gr.
(rpm)
(watt)
(Nm)
(Nl/min.)
(Kg)
(dB(A))
(m/s
2
)
ERVIT11
8302061 2000 130
1,4
420
0.88
76.5
<1
7311141
ERVIT22
8302062 800 130 3,6
420
1,05 76.5
<1
7311142
ERVIT33
8302063 450 130 6,5
420
1,05 76.5
<1
7311142
ERVIT44
8302064 250 130 11.5
420
1,05 76.5
<1
7311143
ERGOVIT22
8302072 1800 220
3,5
680
0.95
74.7
<1
7311142
ERGOVIT25
8302074 1000 220
6,3
680
1.1
74.7
<1
7311143
ERGOVIT33
8302073 670 220 8,8
680
1.1
74.7
<1
7311143
ERGOVIT55
8302075 380 220 15,7
680
1.1
74.7
<1
7311143
ERGOVIT77
8302077 210 220 28
680
1.1
74.7
<1
7311144
SUPERGOVIT2 8302066 1700 440
8
750
1.19
80.3
<1
7311143
SUPERGOVIT3 8302067 670 440 20
750
1.37 80.3
<1
7311144
SUPERGOVIT5 8302068 380 440 36
750
1.37 80.3
<1
7311144
Air inlet 1/4 GAS - Ø inside tube min. ERVIT 6 mm; ERGOVIT 8 mm SUPERGOVIT 10 mm - 1/4" hexagonal connection
(6.35 mm)
Noise emission levels determined by using ISO/CD15744
Levels of vibrations at the handle determined by using ISO8662
Note: make sure that the performance features required correspond to those described above, otherwise it will be
necessary to choose a different model from the broad range offered by OBER.
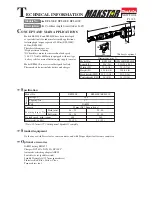
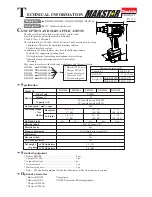
CLUTCH
The gear clutch is mounted on the tool-bearing spindle in the front part of the screwdriver.
It has the function of transmitting to the bit, and therefore to the screw, only part of the torque
that may be produced by the screwdriver so as to ensure optimal screw-tightening conditions.
It also makes it possible to maintain a highly constant level of torque when tightening screws
in sequence. When the resistance offered by the screw has reached the maximum level
allowed by the clutch setting, the teeth skip to prevent the torque transmitted from exceeding
the preset level. The range of clutch settings is determined by the spring (1) that locks the
toothed disks (2). Different springs are available, each one covering a range of torque values
as indicated in table 2. Note that the ranges of torque settings are overlapping, i.e. certain
torque values may be obtained with different springs. When choosing a spring, it is always
advisable to make sure that the levels of torque you wish to obtain are situated towards the
middle of its range of settings. With the same screwdriver and the same spring, the effective
torque applied to the screw strongly depends on the degree of rigidity of the joint. Other conditions being equal, pliable or
elastic joints may determine a considerable reduction in torque. All the values shown in the diagrams and tables refer to
rigid joints. Each screwdriver is supplied with the clutch specified in table 1. If you should wish to obtain a level of torque
outside its range of settings, you may request other clutches or springs as indicated in table in 2.
Table 2
RANGE OF CLUTCH SETTINGS
Clutch group
Spring code
Spring colour
Torque
7311146
5080111
green
7311141
5080110
white
7311142
5080112
yellow
7311143
5080114
plain
7311144
5080116
red
7311145
5080118
black
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
13
14
15 16 17 18 Nm