9. VLAN Configuration
NetXen, Inc.
Intelligent NIC Getting Started Guide — NDA Required
33
9
VLAN Configuration
9.1
Windows
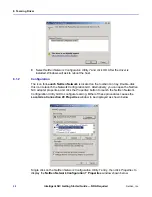
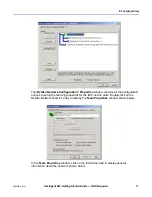
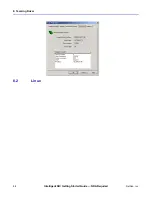
This section describes the NIC VLAN on Windows using the miniport driver (NIC Driver).
The IM Driver GUI can set multiple VLAN IDs, unlike the NIC Driver property sheet. The
VLAN decision tables shown below describe how the packets are handled by the NIC
driver.
9.1.1
NIC VLAN as Send Side
To generate the components of the packet's tag header a miniport driver:
1
Sets the tag header's CFI bit to zero.
2
Proceed as indicated in the following table, based on the following values:
Configured VLAN ID for the NIC.
Priority or VLAN ID in the packet's OOB data.
VLAN ID in the packet's tag header.
If the priority value that the miniport driver retrieves from the packet is zero, the miniport
driver should not mark the packet with a priority value before transmitting the packet over
the network. On Ethernet (802.3) networks, an unmarked packet is the same as a packet
that is marked with the "best effort" priority value appended to it. Not marking packets
ensures backward compatibility with devices on the network that do not support the tag
header.
Table 7 NIC VLAN as Send Side
Configured VLAN
ID for the NIC
Priority or VLAN ID in the
Packet's OOB Data
VLAN ID in the
Packet's Tag Header
Miniport Driver Action
Zero
Priority and VLAN ID are
zero.
Any value or not present
Send the packet with no changes.
Zero
Priority or VLAN ID is
nonzero.
Not present
Insert tag header into packet.Set
VLAN ID in tag header to the value of
VLAN ID in OOB data.Send packet.
Nonzero
VLAN ID is zero or matches
the configured VLAN ID for
the NIC.
Not present
Insert tag header into packet.Set
VLAN ID in tag header to the value of
configured VLAN ID for the
NIC.Send packet.
Nonzero
VLAN ID matches the
configured VLAN ID for the
NIC.
Zero
Set VLAN ID in tag header to the
value of configured VLAN ID for the
NIC.Send packet.
Nonzero
Not present.
Matches the configured
VLAN ID for the NIC.
Send the packet with no changes.