Register Map and Descriptions
Appendix D
Lab-PC+ User Manual
D-40
© National Instruments Corporation
Interval Counter Strobe Register
Writing to Interval Counter Strobe Register strobes the contents of the Interval Counter Data
Register into the Interval Counter. This action arms the Interval Counter, which then decrements
with each conversion pulse.
Address:
Base a 1F (hex)
Type:
Write-only
Word Size:
8-bit
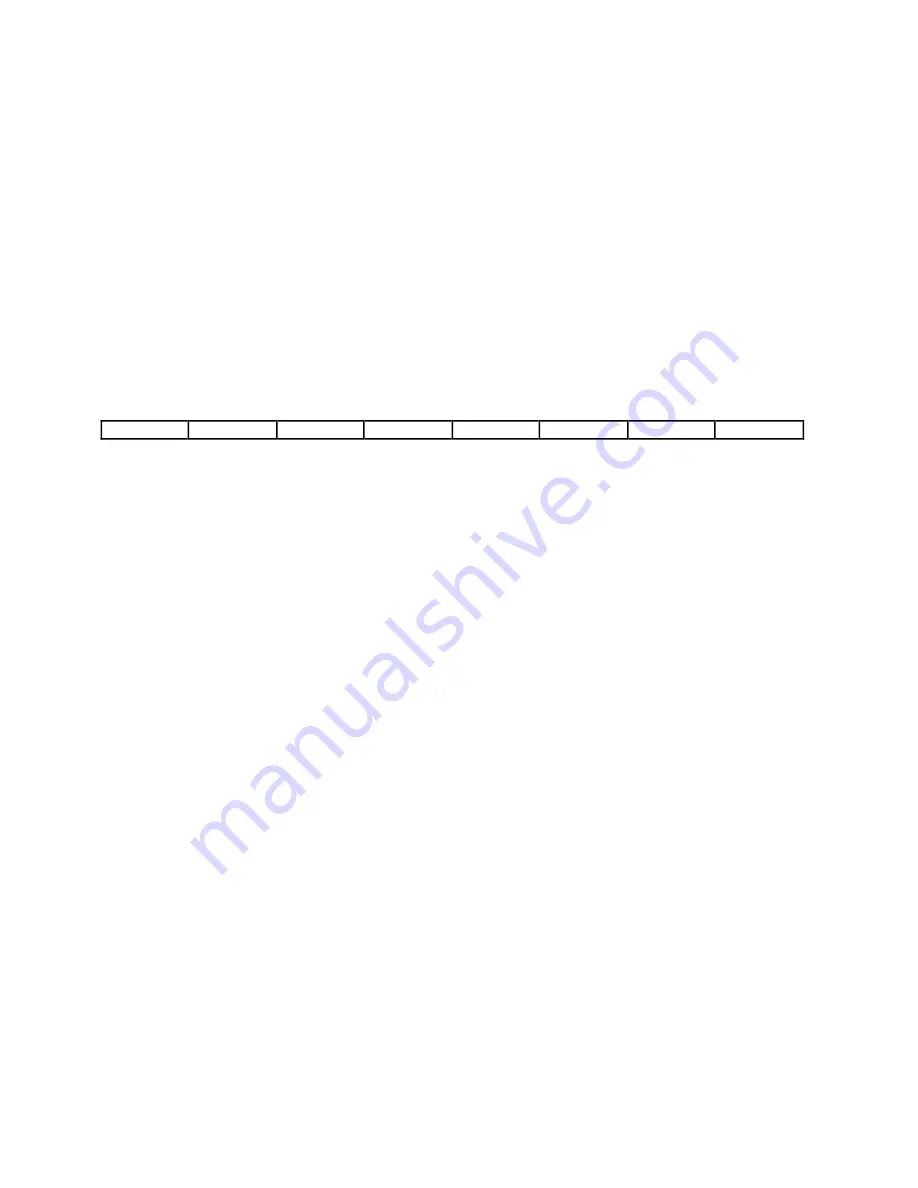
Bit Map:
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
Bit
Name
Description
7-1
0
Each of these bits must be 0 for proper operation of the Lab-PC+.
0
1
This bit must be 1 for proper operation of the Lab-PC+.
Summary of Contents for Lab-PC+
Page 89: ......
Page 90: ......
Page 91: ......
Page 92: ......
Page 93: ......
Page 94: ......
Page 95: ......
Page 96: ......
Page 97: ......
Page 98: ......
Page 99: ......
Page 101: ......
Page 102: ......
Page 103: ......
Page 104: ......
Page 105: ......
Page 106: ......
Page 107: ......
Page 108: ......
Page 109: ......
Page 110: ......
Page 111: ......
Page 112: ......
Page 113: ......
Page 114: ......
Page 115: ......
Page 116: ......
















































