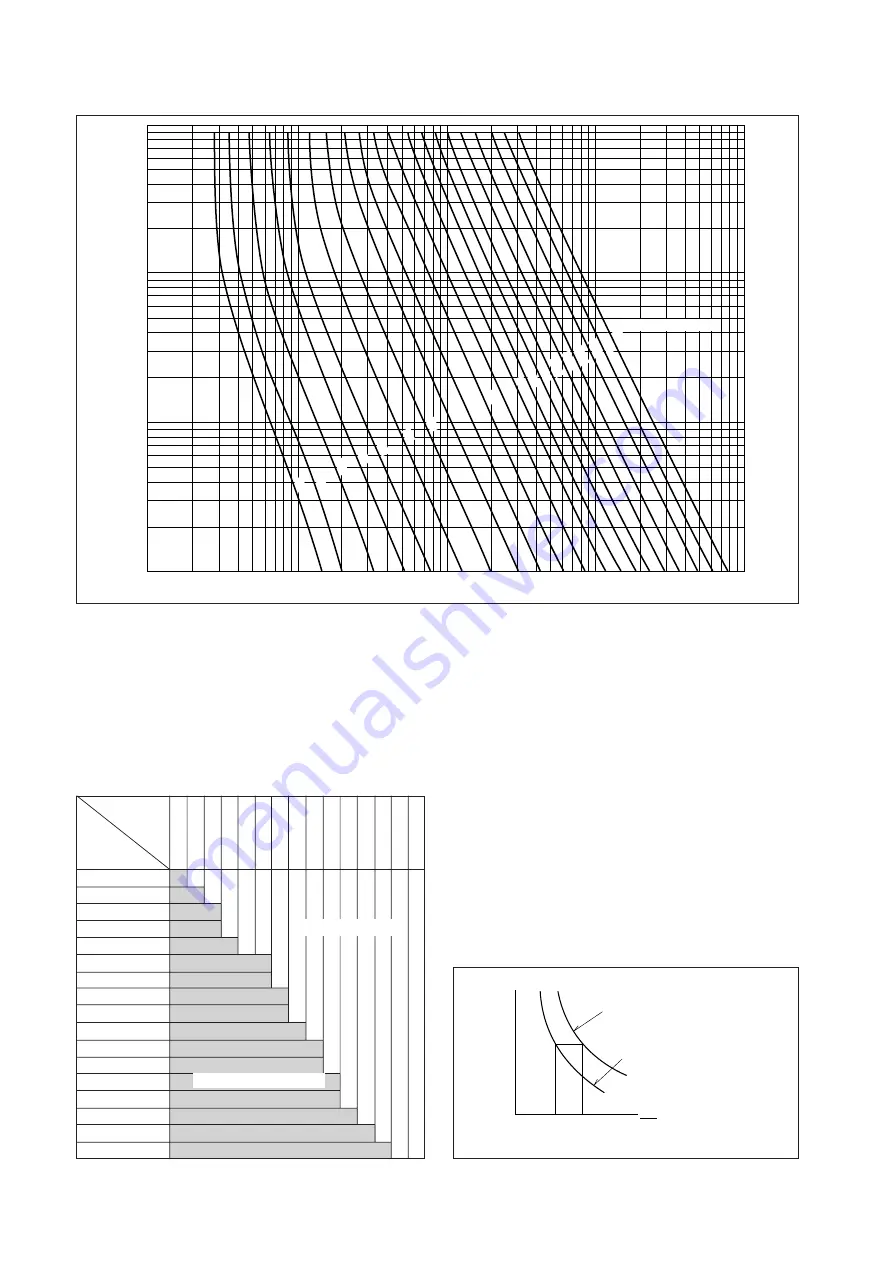
50
Fig. 6.14 Relation of Let-through Current to Time until 600V Vinyl-Insulated Wire Reaches a 70
°
C Temperature Rise.
(In a Start from No Load State at Ambient Temperature of 30
°
C)
Fig. 6.15 MCCBs and Wiring Sizes
15
20
30
40
50
60
75
100
125
150
175
200
225
250
300
350
400
Wire size
(mm
2
)
MCCB
rating(A)
1
1.5
2.5
4
6
10
16
25
35
50
70
95
120
185
240
Unprotected region
Protected region
Fig. 6.16 Wire Derating Method, for Conduit Routing
Current (
×
10
2
A)
Time (sec)
1000
800
600
500
10
0.2
0.4 0.5 0.6
0.3
1
0.8
2
3
10
9
20
30 40 50
100
1000
200
300
500
80
60
8
7
6
5
4
0.1
6
5
4
3
2
1
20
30
40
50
60
100
200
300
400
630
185
150
120
95
70
50
35
25
16
10
6.0
4.0
2.5
1.5
1.0
500
400
300
240
Wire sizes (mm
2
)
=Correction factor
Time.
!
2
!
1
!
1
!
2
Current
Open wiring
Routed in conduit
ground use; ultimately, the temperature figure of 75
°
C
is derived (100
°
C per Jones and Scott, compensated)
as a suitable short-time limitation for wiring with heat-
proof vinyl or styrene-butadene-rubber insulation.
Current transpositions for the range of wire sizes are
not presented, being non-standard ; however, Fig. 6.15
gives MCCB ratings for temperature limitations of 30
°
C
in normal operation, and 75
°
C for periods of up to 20
seconds.
The apparent disparity of the ambient ratings of 30
°
C
for wiring against 40
°
C for MCCBs, is reconcilable in
that wiring, for the most part, is externally routed, while
MCCBs are housed in panelboards or the like. The
two figures can be used compatibly, without modifi-
cation. It is further noted that, where MCCBs with long-
delay elements of the thermal type are employed, the
effect of increased ambient, which would normally
derate the wiring, is adequately compensated by the
attendant decrease in thermal-region tripping time of
the MCCB.
The curves in Fig. 6.17 show the comparison of the
delay regions of MCCB tripping with allowable cur-
rents in open-routed wiring. Fig. 6.16 shows the
method required by the Japanese standards referred
to above, for derating wiring to be routed in conduit.



































