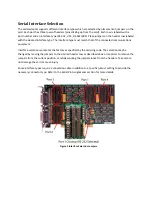
Differential
Fail
Safe
Biasing
Fail
‐
safe
biasing
is
a
technique
that
guarantees
differential
input
signals
are
in
a
steady
state
when
not
connected
to
an
active
differential
output.
Optional
fail
‐
safe
biasing
of
all
differential
inputs
(RS
‐
422/RS
‐
485/V.11)
for
a
port
is
available
by
installing
a
resistor
pack
in
the
socket
labeled
‘FAILSAFE’.
This
resistor
pack
is
not
included
by
default
with
the
hardware.
Contact
MicroGate
sales
to
request
fail
‐
safe
resistor
packs
when
ordering
the
hardware.
Fail
‐
safe
biasing
is
only
used
when
an
input
is
not
constantly
driven
by
an
output,
and
that
input
is
terminated
(see
previous
section
on
differential
input
termination).
When
an
input
is
not
terminated,
fail
‐
safe
biasing
integral
to
each
receiver
circuit
maintains
the
input
in
a
steady
state.
When
an
input
is
terminated,
external
fail
‐
safe
biasing
(resistor
pack)
may
be
required
to
guarantee
the
input
is
in
a
steady
state.
An
example
application
that
uses
fail
‐
safe
biasing
is
bus
mode
connections
where
a
single
cable
conductor
pair
is
connected
to
both
the
transmit
data
output
and
receive
data
input
for
more
than
one
station.
In
this
setup,
only
one
output
may
be
active
at
the
same
time
and
each
output
is
only
driven
when
sending
data.
When
no
station
is
sending,
the
external
fail
‐
safe
biasing
maintains
a
voltage
on
the
cable
pair
that
keeps
inputs
in
a
steady
state.
WARNING
:
Fail
‐
safe
biasing
must
be
present
on
only
a
single
station
connected
to
a
cable
pair.
This
single
station
maintains
the
voltage
on
the
cable
to
keep
all
connected
inputs
in
a
steady
state.
Applying
fail
‐
safe
biasing
at
multiple
points
on
a
cable
may
result
in
incorrect
operation.
Figure
4 Fail
Safe
Biasing
Sockets