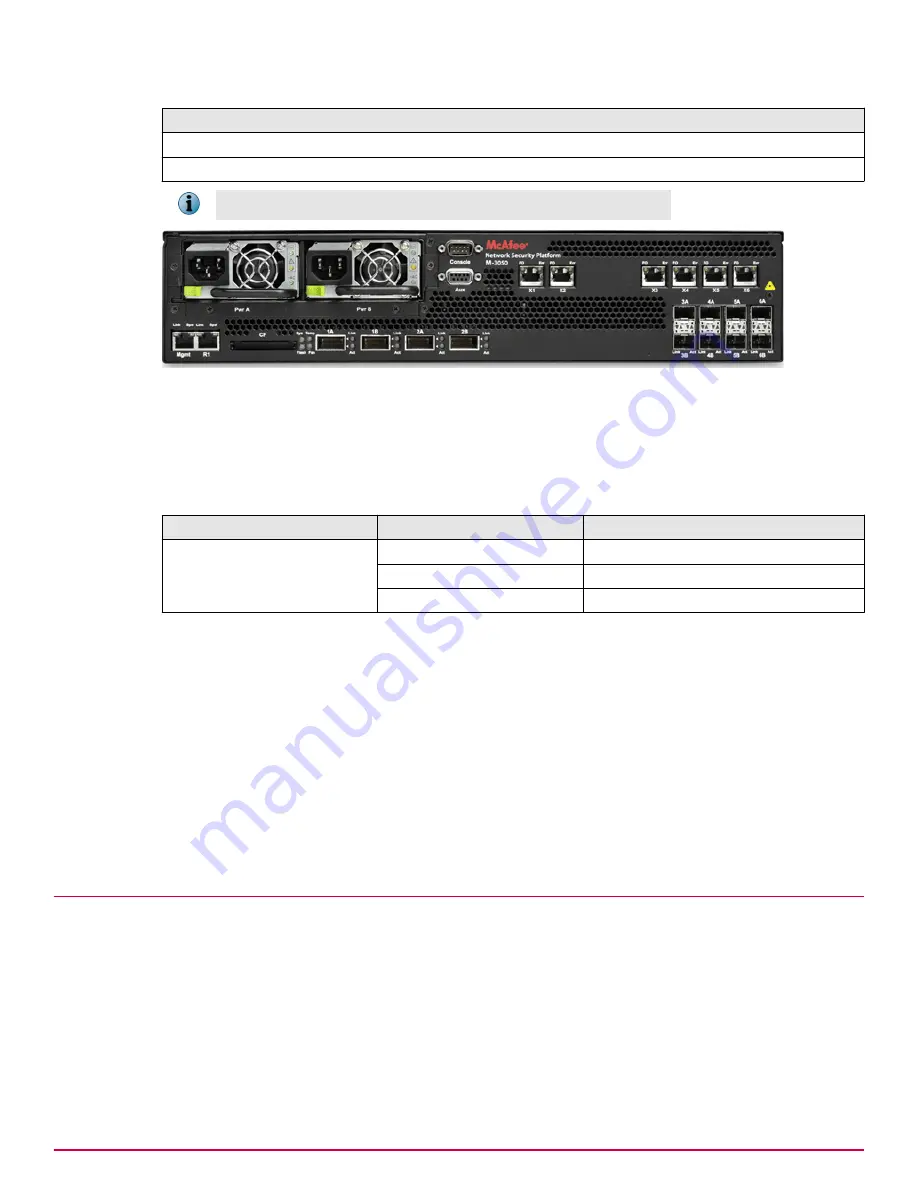
Port Pairs (and Transceiver Type)
5A and 5B (SFP)
6A and 6B (SFP)
You cannot configure, for example, IA and 2A to work together as a pair.
Figure 4-1 Using peer ports
Default Monitoring port speed settings
Make sure that the settings on the network devices match the settings on the Sensor Monitoring ports
to which they are connected.
Table 4-1 Default Monitoring port speed settings
Monitoring Ports
Operating Mode
Speed/Duplex Setting
XFP ports
SFP ports
SPAN
Auto-negotiation is ON.
Tap
Auto-negotiation is ON.
In-line
Auto-negotiation is ON.
Cable types for routers, switches, hubs, and PCs
This section lists the types of cables that you require to connect the Sensor to other network devices:
• Use a crossover Ethernet RJ-45 cable to connect a router port to the 10/100/1000 copper SFP
monitoring ports.
• Use a straight-through Ethernet RJ-45 cable to connect a switch or a hub port to 10/100/1000
copper SFP monitoring ports.
• Use a crossover Ethernet RJ-45 cable to connect a router port to PC to the Sensor Management
port.
• Use a crossover Ethernet RJ-45 cable to connect a PC to the Sensor monitoring port.
Connect the cables for in-line mode
The Gigabit Ethernet ports fail-close, meaning they stop the flow of traffic if the Sensor fails. To allow
traffic to flow uninterrupted, you must use special hardware, and cable the Sensor to fail-open. For
instructions, see the subsequent sections of this chapter.
This section provides the steps to connect the Sensor's Gigabit Ethernet ports so they fail-close.
4
Attaching Cables to the Sensor
Connect the cables for in-line mode
30
McAfee
®
Network Security Platform
M-3050/M-4050 Sensor Product Guide































